UpGrid: Integración Flexible de Generación Distribuida en Redes de Baja y Media Tensión Mediante Sistemas de Control Avanzados (Portugal)
Contenido principal del artículo
Resumen
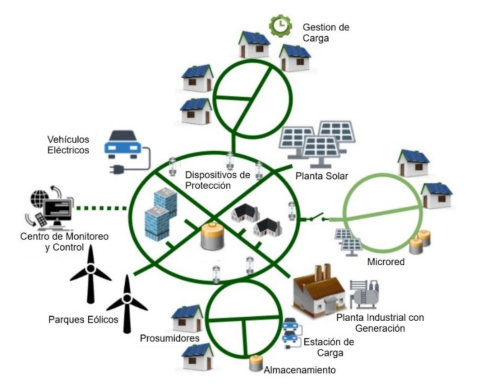
Las redes eléctricas de baja tensión (BT) todavía se manejan con métodos tradicionales, lo que limita la visibilidad de los flujos de potencia y tensión, así como el entendimiento de la conectividad y la automatización de las operaciones. En este contexto, el proyecto UPGRID presenta una propuesta abierta y completa que busca modernizar la distribución eléctrica, generando beneficios operativos y nuevas oportunidades de negocio para todos los actores del sector, incluidos los consumidores finales. Su meta es dotar al sistema eléctrico de productos y servicios innovadores que optimicen la gestión de la red, reduzcan los tiempos de restauración del suministro y ofrezcan información precisa en tiempo real, facilitando además la participación activa en el mercado energético. Basado en la iniciativa InovGrid, el proyecto se estructura en tres pilares: medición inteligente, redes inteligentes enfocadas en la eficiencia y la confiabilidad, y microgeneración, incorporando tecnologías existentes para fortalecer la monitorización, el control y la seguridad.
Detalles del artículo

Esta obra está bajo una licencia internacional Creative Commons Atribución-NoComercial-SinDerivadas 4.0.
Citas
P. Cunha, S. Almeida Neves, A. Cardoso Marques, y Z. Serrasqueiro, «Adoption of energy efficiency measures in the buildings of micro-, small- and medium-sized Portuguese enterprises», Energy Policy, vol. 146, p. 111776, nov. 2020, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2020.111776.
J. Crispim, J. Braz, R. Castro, y J. Esteves, «Smart Grids in the EU with smart regulation: Experiences from the UK, Italy and Portugal», Utilities Policy, vol. 31, pp. 85-93, dic. 2014, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jup.2014.09.006.
L. E. Rielli y I. Campos, «The process matters: Exploring public participation in solar energy projects in Brazil and Portugal», Energy Research & Social Science, vol. 125, p. 104078, jul. 2025, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.erss.2025.104078.
C. Gouveia, D. Rua, F. J. Soares, C. Moreira, P. G. Matos, y J. A. Peças Lopes, «Development and implementation of Portuguese smart distribution system», Electric Power Systems Research, vol. 120, pp. 150-162, mar. 2015, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsr.2014.06.004.
R. Pereira, J. Figueiredo, R. Melicio, V. Mendes, J. Martins, y J. C. Quadrado, «Consumer energy management system with integration of smart meters», Energy Reports, vol. 1, pp. 22-29, nov. 2015, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egyr.2014.10.001.
I. L. R. Gomes, M. G. Ruano, y A. E. Ruano, «MILP-based model predictive control for home energy management systems: A real case study in Algarve, Portugal», Energy and Buildings, vol. 281, p. 112774, feb. 2023, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enbuild.2023.112774.
Y. Chawla, A. Kowalska-Pyzalska, y P. Duarte Silveira, «Marketing and communications channels for diffusion of electricity smart meters in Portugal», Telematics and Informatics, vol. 50, p. 101385, jul. 2020, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tele.2020.101385.
F. W. Geels, S. Sareen, A. Hook, y B. K. Sovacool, «Navigating implementation dilemmas in technology-forcing policies: A comparative analysis of accelerated smart meter diffusion in the Netherlands, UK, Norway, and Portugal (2000-2019)», Research Policy, vol. 50, n.o 7, p. 104272, sep. 2021, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.respol.2021.104272.
F. Iberraken, R. Medjoudj, y D. Aissani, «Decision Making on Smart Grids Projects Moving using AHP Method: The case of Algerian Network», IFAC Proceedings Volumes, vol. 46, n.o 9, pp. 543-548, 2013, https://doi.org/10.3182/20130619-3-RU-3018.00524.
M. A. R. Lopes, C. H. Antunes, K. B. Janda, P. Peixoto, y N. Martins, «The potential of energy behaviours in a smart(er) grid: Policy implications from a Portuguese exploratory study», Energy Policy, vol. 90, pp. 233-245, mar. 2016, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2015.12.014.
M. Shakeri et al., «Implementation of a novel home energy management system (HEMS) architecture with solar photovoltaic system as supplementary source», Renewable Energy, vol. 125, pp. 108-120, sep. 2018, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2018.01.114.
J. B. Santos, R. Scharnigg, J. Monteiro, y A. Pacheco, «Fair shares or smart savings? Exploring business models, justice and efficiency trade-offs in Portuguese energy communities», Energy Research & Social Science, vol. 125, p. 104102, jul. 2025, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.erss.2025.104102.
F. Alassery, «Advanced metering infrastructure smart metering based on cloud architecture for low voltage distribution networks in application of smart grid monitoring», Sustainable Computing: Informatics and Systems, vol. 35, p. 100747, sep. 2022, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.suscom.2022.100747.
R. Qi, Q. Li, Z. Luo, J. Zheng, y S. Shao, «Deep semi-supervised electricity theft detection in AMI for sustainable and secure smart grids», Sustainable Energy, Grids and Networks, vol. 36, p. 101219, dic. 2023, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.segan.2023.101219.
P. D. Halle y S. Shiyamala, «Secure advance metering infrastructure protocol for smart grid power system enabled by the Internet of Things», Microprocessors and Microsystems, vol. 95, p. 104708, nov. 2022, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micpro.2022.104708.
F. Ghanavati, G. J. Osório, J. C. O. Matias, y J. P. S. Catalão, «Transactive data-driven and consumer-centric home energy management system for local energy communities in Portugal», Sustainable Cities and Society, vol. 131, p. 106698, sep. 2025, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scs.2025.106698.
E. Efatinasab, N. Azadi, G. A. Susto, C. M. Ahmed, y M. Rampazzo, «Fortifying smart grid stability: Defending against adversarial attacks and measurement anomalies», Sustainable Energy, Grids and Networks, vol. 43, p. 101799, sep. 2025, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.segan.2025.101799.
K. Gupta, V. Kumar, y R. Prakash, «An Efficient Approach to Key Management for Bidirectional Communication in AMI System of Smart Grids», Procedia Computer Science, vol. 259, pp. 1179-1188, 2025, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2025.04.073.
The European Parliament and the Council of the European Union, Directiva (UE) 2019/944 del Parlamento Europeo y del Consejo, de 5 de junio de 2019, sobre normas comunes para el mercado interior de la electricidad y por la que se modifica la Directiva 2012/27/UE, vol. 158. 2019, pp. 125-199. [En línea]. Disponible en: http://data.europa.eu/eli/dir/2019/944/oj/spa
European Commission, «Standardization Mandate to European Standardisation Organisations (ESOs) to support European Smart Grid deployment», CEN-CENELEC-ETSI, Brussels, mar. 2011. [En línea]. Disponible en: https://www.cencenelec.eu/media/CEN-CENELEC/AreasOfWork/CEN-CENELEC_Topics/Smart%20Grids%20and%20Meters/Smart%20Grids/m490_smart-grids_mandate.pdf?utm_source=chatgpt.com