UpGrid: Flexible Integration of Distributed Generation in Low- and Medium Voltage Networks through Advanced Control Systems (Portugal)
Main Article Content
Abstract
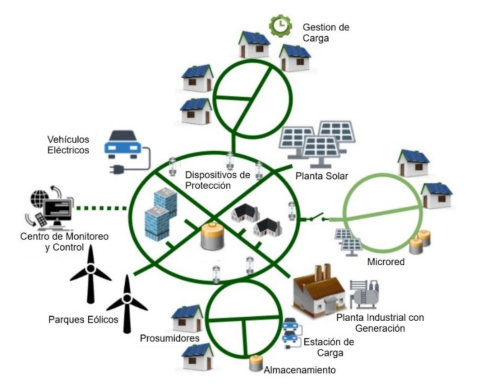
Low-voltage (LV) electrical networks are still being managed with traditional methods, which really limits how well we can see power and voltage flows, understand network connectivity, and automate operations. In this light, the UPGRID project steps in with a bold and comprehensive plan to modernize electrical distribution. This initiative aims to create operational benefits and open up new business opportunities for everyone involved in the sector, including end consumers. The project's mission is to equip the electrical system with cutting-edge products and services that enhance network management, shorten supply restoration times, and deliver precise real-time information, all while encouraging active participation in the energy market. Building on the InovGrid initiative, UPGRID is built around three key pillars: smart metering, intelligent networks that prioritize efficiency and reliability, and microgeneration, all designed to leverage existing technologies for better monitoring, control, and security.
Downloads
Metrics
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
References
P. Cunha, S. Almeida Neves, A. Cardoso Marques, y Z. Serrasqueiro, «Adoption of energy efficiency measures in the buildings of micro-, small- and medium-sized Portuguese enterprises», Energy Policy, vol. 146, p. 111776, nov. 2020, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2020.111776.
J. Crispim, J. Braz, R. Castro, y J. Esteves, «Smart Grids in the EU with smart regulation: Experiences from the UK, Italy and Portugal», Utilities Policy, vol. 31, pp. 85-93, dic. 2014, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jup.2014.09.006.
L. E. Rielli y I. Campos, «The process matters: Exploring public participation in solar energy projects in Brazil and Portugal», Energy Research & Social Science, vol. 125, p. 104078, jul. 2025, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.erss.2025.104078.
C. Gouveia, D. Rua, F. J. Soares, C. Moreira, P. G. Matos, y J. A. Peças Lopes, «Development and implementation of Portuguese smart distribution system», Electric Power Systems Research, vol. 120, pp. 150-162, mar. 2015, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsr.2014.06.004.
R. Pereira, J. Figueiredo, R. Melicio, V. Mendes, J. Martins, y J. C. Quadrado, «Consumer energy management system with integration of smart meters», Energy Reports, vol. 1, pp. 22-29, nov. 2015, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egyr.2014.10.001.
I. L. R. Gomes, M. G. Ruano, y A. E. Ruano, «MILP-based model predictive control for home energy management systems: A real case study in Algarve, Portugal», Energy and Buildings, vol. 281, p. 112774, feb. 2023, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enbuild.2023.112774.
Y. Chawla, A. Kowalska-Pyzalska, y P. Duarte Silveira, «Marketing and communications channels for diffusion of electricity smart meters in Portugal», Telematics and Informatics, vol. 50, p. 101385, jul. 2020, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tele.2020.101385.
F. W. Geels, S. Sareen, A. Hook, y B. K. Sovacool, «Navigating implementation dilemmas in technology-forcing policies: A comparative analysis of accelerated smart meter diffusion in the Netherlands, UK, Norway, and Portugal (2000-2019)», Research Policy, vol. 50, n.o 7, p. 104272, sep. 2021, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.respol.2021.104272.
F. Iberraken, R. Medjoudj, y D. Aissani, «Decision Making on Smart Grids Projects Moving using AHP Method: The case of Algerian Network», IFAC Proceedings Volumes, vol. 46, n.o 9, pp. 543-548, 2013, https://doi.org/10.3182/20130619-3-RU-3018.00524.
M. A. R. Lopes, C. H. Antunes, K. B. Janda, P. Peixoto, y N. Martins, «The potential of energy behaviours in a smart(er) grid: Policy implications from a Portuguese exploratory study», Energy Policy, vol. 90, pp. 233-245, mar. 2016, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2015.12.014.
M. Shakeri et al., «Implementation of a novel home energy management system (HEMS) architecture with solar photovoltaic system as supplementary source», Renewable Energy, vol. 125, pp. 108-120, sep. 2018, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2018.01.114.
J. B. Santos, R. Scharnigg, J. Monteiro, y A. Pacheco, «Fair shares or smart savings? Exploring business models, justice and efficiency trade-offs in Portuguese energy communities», Energy Research & Social Science, vol. 125, p. 104102, jul. 2025, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.erss.2025.104102.
F. Alassery, «Advanced metering infrastructure smart metering based on cloud architecture for low voltage distribution networks in application of smart grid monitoring», Sustainable Computing: Informatics and Systems, vol. 35, p. 100747, sep. 2022, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.suscom.2022.100747.
R. Qi, Q. Li, Z. Luo, J. Zheng, y S. Shao, «Deep semi-supervised electricity theft detection in AMI for sustainable and secure smart grids», Sustainable Energy, Grids and Networks, vol. 36, p. 101219, dic. 2023, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.segan.2023.101219.
P. D. Halle y S. Shiyamala, «Secure advance metering infrastructure protocol for smart grid power system enabled by the Internet of Things», Microprocessors and Microsystems, vol. 95, p. 104708, nov. 2022, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micpro.2022.104708.
F. Ghanavati, G. J. Osório, J. C. O. Matias, y J. P. S. Catalão, «Transactive data-driven and consumer-centric home energy management system for local energy communities in Portugal», Sustainable Cities and Society, vol. 131, p. 106698, sep. 2025, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scs.2025.106698.
E. Efatinasab, N. Azadi, G. A. Susto, C. M. Ahmed, y M. Rampazzo, «Fortifying smart grid stability: Defending against adversarial attacks and measurement anomalies», Sustainable Energy, Grids and Networks, vol. 43, p. 101799, sep. 2025, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.segan.2025.101799.
K. Gupta, V. Kumar, y R. Prakash, «An Efficient Approach to Key Management for Bidirectional Communication in AMI System of Smart Grids», Procedia Computer Science, vol. 259, pp. 1179-1188, 2025, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2025.04.073.
The European Parliament and the Council of the European Union, Directiva (UE) 2019/944 del Parlamento Europeo y del Consejo, de 5 de junio de 2019, sobre normas comunes para el mercado interior de la electricidad y por la que se modifica la Directiva 2012/27/UE, vol. 158. 2019, pp. 125-199. [En línea]. Disponible en: http://data.europa.eu/eli/dir/2019/944/oj/spa
European Commission, «Standardization Mandate to European Standardisation Organisations (ESOs) to support European Smart Grid deployment», CEN-CENELEC-ETSI, Brussels, mar. 2011. [En línea]. Disponible en: https://www.cencenelec.eu/media/CEN-CENELEC/AreasOfWork/CEN-CENELEC_Topics/Smart%20Grids%20and%20Meters/Smart%20Grids/m490_smart-grids_mandate.pdf?utm_source=chatgpt.com