Análisis del Modelo de Desgaste Lineal de Archard, una Vista Dinámica al Modelo Original
Contenido principal del artículo
Resumen
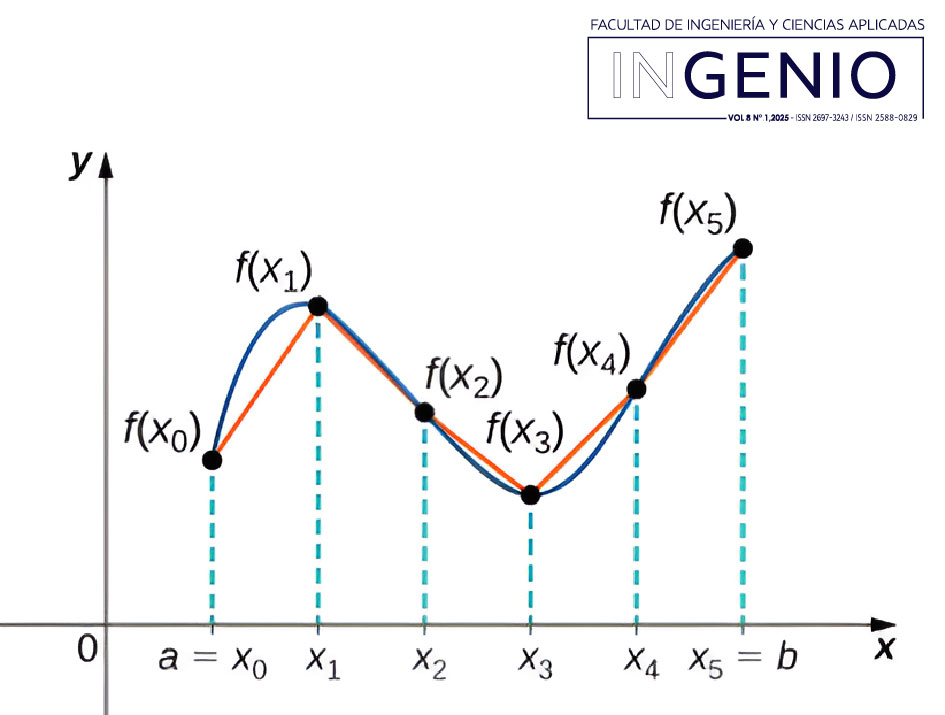
El modelo Archard es un modelo lineal que describe el desgaste de un sistema deslizante. Sin embargo, si se desea aplicar este modelo a un sistema oscilante, se deben considerar algunas modificaciones y el uso de ecuaciones diferenciales puede ser una estrategia útil. En un sistema oscilante, las superficies de contacto realizan movimientos repetitivos hacia adelante y hacia atrás. Esto puede cambiar la forma en que se produce el desgaste porque las superficies pueden desgastarse en diferentes áreas. Además, la carga aplicada puede cambiar durante el ciclo de oscilación de una pieza, lo que también puede afectar al desgaste.
Para modelar este tipo de sistema, podría considerar el uso de ecuaciones diferenciales ordinarias o parciales, según la complejidad del sistema. Estas ecuaciones le permitirán modelar cómo cambia el desgaste de elementos metálicos con el tiempo y cómo depende de factores como la posición y la velocidad en el ciclo de vibración.
Descargas
Métricas
Detalles del artículo

Esta obra está bajo una licencia internacional Creative Commons Atribución-NoComercial-SinDerivadas 4.0.
Citas
Alexander, F., Bustamante, S., Manuel, J., Restrepo, V. (2004). Estudio del modelo de desgaste propuesto por Archard. http://www.redalyc.org/articulo.oa?id=49614603
Arroyo, A. Imbaquingo, K. (2023). Modelización matemática del desgaste en pastillas de freno de vehículos. Universidad técnica del norte.
Da Silva, C. R. Á., & Pintaude, G. (2008). Uncertainty analysis on the wear coefficient of the Archard model. Tribology International, 41(6), 473–481. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2007.10.007 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2007.10.007
Mattei, L., Francesco Di Puccio, F. (2023). How accurate is the Archard law to predict wear of UHMWPE in hard-on-soft hip implants? A numerical and experimental investigation. Tribology International, 187. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2023.108768 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2023.108768
Santana Reyes, S. A., Santana Milán, R., Guardia Puebla, Y., & Morales Leslie, J. F. (2019). Determinación de los principales factores geométricos que influyen en el desgaste de las matrices de extrusión directa empleadas en la obtención en frío de perfiles de aleaciones de aluminio. Ingeniería Investigación y Tecnología, 20(4), 1–11. https://doi.org/10.22201/fi.25940732e.2019.20n4.037 DOI: https://doi.org/10.22201/fi.25940732e.2019.20n4.037
Jimenez Torrado, (2009). Comparación del desgaste por abrasión y el desgaste por deslizamiento de los aceros AISI/SAE 1020, 1045 y 4140, según las normas ASTM G65 Y G99. Facultad de ingeniería departamento de ingeniería mecánica.
Romero Contreras, J. E., & Cabello Sequera, S. B. (2020). Comportamiento ante el desgaste por deslizamiento en seco del acero inoxidable súper dúplex en un tribómetro bola sobre anillo. Revista Colombiana de Biotecnología, 22(1), 6–17. https://doi.org/10.15446/rev.colomb.biote.v22n1.60835 DOI: https://doi.org/10.15446/rev.colomb.biote.v22n1.60835
Mariana Nieto, (2015). DISEÑO DE UN MODELO FÍSICO APLICANDO ECUACIONES DIFERENCIALES.tesis.pdf (unam.mx)
Juan Beltran (2022). Longitud del arco de una curva y área de una superficie. https://calculo21.com/longitud-del-arco-de-una-curva-y-area-de-una-superficie/
Miguel Rodriguez, 2022. Cálculo Diferencial e Integral II: Longitud de arco
Cálculo Diferencial e Integral II: Longitud de arco - El blog de Leo (nekomath.com)
Mena, Granizo, Hernandez, Audelo (2023) Cálculo de la velocidad de desgaste abrasivo en engranajes de dientes rectos y helicoidales con perfil evolvente, utilizando una GUI de Matlab.http://scielo.senescyt.gob.ec/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S1390-860X2023000100032
Vedan Alex (2023), La importancia de la lubricación industrial. https://tractian.com/es/blog/lubricacion-industrial-analicemos-los-diferentes-tipos-de-lubricantes-y-su-importancia
Ramírez-Cuellar, Jorge & Chavela, Julio & SANDOVAL-CABALLERO, IGNACIO & CANTU-RANGEL, MIGUEL & OLVERA-BRISEÑO, JOSE. (2003). DESGASTE EN RODILLOS DE TRABAJO ICDP, HSS, HICR EN EL CUARTO CASTILLO EN UN LAMINADOR TIPO COMPACTO Y UNO CONVENCIONAL DE PRODUCTOS PLANOS.
Ruíz Zelada, Marco (2000). COMPENDIO DE NORMAS PARA PRODUCTOS DE ACERO.
Struers Ensuring Certainty (s.f.). Ensayos de Dureza. https://www.struers.com/es-ES/Knowledge/Hardness-testing#