Entomopathogenic bacteria and fungi in the management of Brevicoryne brassicae (Homoptera: Aphididae) in cabbage crops
Main Article Content
Abstract
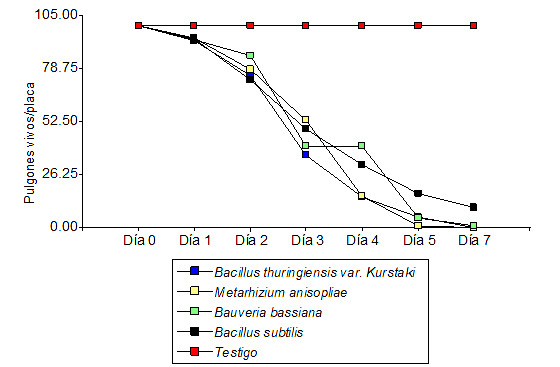
The use of fungi and bacteria with pathogenic capacity towards insects is considered a sustainable agroecological alternative for efficient pest control, as they are microorganisms of easy production in industrial scale, formulation and use. Therefore, the objective was to evaluate four entomopathogenic formulations in the control of Brevicoryne brassicae L., a key pest of cabbage (Brassica oleracea L.), in a randomized complete block design with 4 treatments, plus an absolute control and 4 replicates. The variables evaluated were the number of dead and live aphids per plant and the number of infested plants. The commercial formulations Biosafe, BesT-K, Metarrizo and Yurak containing strains of Bacillus subtilis, Bacillus thuringiensis var kurstaki (Btk), Metarhizium anisopliae and Bauveria bassiana respectively, are the ones that were used by spray application to the crop in two seasons: planting, season August-December 2019 and August-December 2021. Among the results, M. anisopliae was recorded with up to 91.11 % efficiency, followed by B. bassiana with 89.50 % and Bs with 79.38 % in the reduction of populations under field conditions. In the laboratory, Btk and M. anisopliae reached 100 % mortality in a period of seven days, so it is concluded that in the medium term, entomopathogenic fungi in the field are more efficient in aphid control; however, in controlled conditions Btk is also efficient.
Downloads
Metrics
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
The authors who publish in Siembra know and accept the following conditions:
- Authors retain the copyright and grant Siembra the right of first publication of the work, under the Creative Commons Attribution License. Third parties are allowed to use what has been published as long as they refer to the author or authors of the work and its publication in this journal.
![]() This content is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial 4.0 International (CC BY-NC 4.0).
This content is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial 4.0 International (CC BY-NC 4.0).
- Authors maintain the copyright and guarantee Siembra the right to publish the manuscript through the channels it considers appropriate.
- Authors may establish on their own additional agreements for the non-exclusive distribution of the version of the work published in Siembra, acknowledging their initial publication in the same, such as in institutional repositories.
- Authors are authorized to disseminate their work electronically once the manuscript is accepted for publication.
References
Abbott, W. S. (1925). A method of computing the effectiveness of an insecticide. Journal of Economic Entomology, 18(2), 265-267. https://doi.org/10.1093/jee/18.2.265a DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/jee/18.2.265a
Al-alawi, M. S., y Obeidat, M. (2014). Selection of Beauveria bassiana (Balsamo) Vuillemin isolates for management of Myzus persicae (sultzar) (hom.: Aphidae) based on virulence and growth-related characteristics. American Journal of Agricultural and Biological Sciences, 9(1), 94-100. https://doi.org/10.3844/ajabssp.2014.94.100 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3844/ajabssp.2014.94.100
Arias, M. J. (2021). Control biológico en insectos plagas de importancia agrícola. En C. Castillo, B. Montero, y P. Cuasapaz (eds.), Memorias del II Congreso de Control Biológico Aplicado (pp. 28-30). rchivos Académicos USFQ. https://doi.org/10.18272/archivosacademicos.vi36.2313 DOI: https://doi.org/10.18272/archivosacademicos.vi36.2313
Askar, S. I. (2021). Efficiency of three coccinellid species against Brevicoryne brassicae (L.) (Homoptera: Aphididae) in cabbage fields at El-Behera Governorate, Egypt. Journal of Plant Protection and Pathology, 12(1), 31-35. https://dx.doi.org/10.21608/jppp.2021.149518 DOI: https://doi.org/10.21608/jppp.2021.149518
Baverstock, J., Roy, H. E., Clark, S. J., Alderson, P. G., y Pell, J. K. (2006). Effect of fungal infection on the reproductive potential of aphids and their progeny. Journal of Invertebrate Pathology, 91(2), 136–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jip.2005.11.005 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jip.2005.11.005
Becerra Verdín, C. A. (2010). Efectividad biológica de Beauveria bassiana y Metarhizium anisopliae (Metsch) Sorokin, sobre pulgones en calabaza japonesa (Cucurbita moschata var. Chirimen). Universidad Autónoma de Nayarit.
Bergamo, R. H. S., Daquila, B. V., y Conte, H. (2019). Sustentabilidade agrícola com fungos entomopatogênicos. En Silva Neto, B. R. da (coord.), Principais grupos e aplicações biotecnológicas dos fungos (pp. 41-52). Atena editora. https://doi.org/10.22533/at.ed.3071918105 DOI: https://doi.org/10.22533/at.ed.3071918105
Boni, S. B., Mwashimaha, R. A., Mlowe, N., Sotelo-Cardona, P., & Nordey, T. (2021). Efficacy of indigenous entomopathogenic fungi against the black aphid, Aphis fabae Scopoli under controlled conditions in Tanzania. International Journal of Tropical Insect Science, 41(2), 1643-1651. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42690-020-00365-8 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42690-020-00365-8
Broekgaarden, C., Poelman, E. H., Steenhuis, G., Voorrips, R. E., Dicke, M., y Vosman, B. (2008). Responses of Brassica oleracea cultivars to infestation by the aphid Brevicoryne brassicae: an ecological and molecular approach. Plant, Cell & Environment, 31(11), 1592-1605. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3040.2008.01871.x DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3040.2008.01871.x
Chakrabarty, S., Chakraborty, P., Islam, T., Aminul Islam, A. K. M., Datta, J., Bhattacharjee, T., Minghui, J., y Xiao, Y. (2022). Bacillus thuringiensis proteins: structure, mechanism and biological control of insect pests. En M. T. Islam, M. Rahman, y P. Pandey (eds.), Bacilli in Agrobiotechnology: Plant Stress Tolerance, Bioremediation, and Bioprospecting (pp. 581-608). Springer International Publishing. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-85465-2_25 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-85465-2_25
Chen, W., Xie, W., Cai, W., Thaochan, N., y Hu, Q. (2021). Entomopathogenic Fungi Biodiversity in the Soil of Three Provinces Located in Southwest China and First Approach to Evaluate Their Biocontrol Potential. Journal of Fungi, 7(11), 984. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof7110984 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/jof7110984
Clifton, E. H., Jaronski, S. T., Coates, B. S., Hodgson, E. W., y Gassmann, A. J. (2018) Efectos de los hongos entomopatógenos endófitos en el pulgón de la soja e identificación de aislados de Metarhizium de campos agrícolas. PLoS ONE, 13(3), e0194815. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0194815 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0194815
Daquila, B. V., Dossi, F. C., Moi, D. A., Moreira, D. R., Caleffe, R. R., Pamphile, J. A., y Conte, H. (2021). Bioactivity of Bacillus thuringiensis (Bacillales: Bacillaceae) on Diatraea saccharalis (Lepidoptera: Crambidae) eggs. Pest Management Science, 77(4), 2019-2028. https://doi.org/10.1002/ps.6230 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/ps.6230
Datta, J., Monsur, M. B., Chakraborty, P., Chakrabarty, S., Fahad, S., Hossain, A., Mondal, F., Ahmed, S., Ali, P., y EL Sabagh, A. (2021). Obstacle in controlling major rice pests in Asia: Insecticide resistance and the mechanisms to confer insecticide resistance. En S. Fahad, O. Sönmez, S. Saud, D. Wang, C. Wu, M. Adnan, M. Arif, Amanullah (eds.), Engineering Tolerance in Crop Plants Against Abiotic Stress (pp. 81-99). CRC Press. https://doi.org/10.1201/9781003160717 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1201/9781003160717-5
Di Rienzo, J. A., Casanoves, F., Balzarini, M. G., Gonzalez, L., Tablada, M., y Robledo, C. W. (2020). InfoStat versión 2020. Centro de Transferencia InfoStat, FCA, Universidad Nacional de Córdoba, Argentina. http://www.infostat.com.ar
Dubrovsky Berensztein, N., Ricci, M., Polack, L. A., y Marasas, M. E. (2017). Control biológico por conservación: evaluación de los enemigos naturales de Brevicoryne brassicae (Hemiptera: Aphididae) en un manejo agroecológico de producción al aire libre de repollo (Brassica oleracea) del Cinturón Hortícola de La Plata, Buenos Aires. Revista de la Facultad de Agronomía, 116(1), 141- 154. http://revista-vieja.agro.unlp.edu.ar/index.php/revagro/article/view/1043
Eidy, M., Rafiee-Dastjerdi, H., Zargarzadeh, F., Golizadeh, A., y Mahdavi, V. (2016). Pathogenicity of the entomopathogenic fungi Beauveria bassiana (Bálsamo) and Verticillium lecanii (Zimmerman) against aphid Macrosiphum rosae, Linnaeus (Hemiptera: Aphididae) under laboratory conditions. Jordan Journal of Biological Sciences, 9(1), 25-28. https://jjbs.hu.edu.jo/files/v9n1/Paper%20Number%203m.pdf DOI: https://doi.org/10.12816/0027004
Ek-Ramos, M. J., Mantzoukas, S., Tamez-Guerra, P., Zavala-Garcia, F., y Lagogiannis, I., (2021). Entomopathogenic fungi tested in planta on pepper and in field on sorghum, to control commercially important species of Aphids. Research Square, PREPRINT (Version 1). https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-745448/v1 DOI: https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-745448/v1
Enríquez Vara, J. N. (2021). Control biológico de plagas con microorganismos entomopatógenos. En J. J. Castañeda Nava (ed.), Tópicos de Herramientas Biotecnológicas para el Desarrollo Agrícola (pp. 73-80). CIATEJ. http://ciatej.repositorioinstitucional.mx/jspui/handle/1023/787
Gebreyohans, G., Chokel, Y., Alemu, T., y Assefa, F. (2021). Management of cabbage aphid (Brevicoryne brassicae L. (Homoptera: Aphididae)) on Ethiopian mustard (Brassica carinata Braun) using entomopathogenic fungi and selected insecticides. SINET: Ethiopian Journal of Science, 44(1), 13-26. https://doi.org/10.4314/sinet.v44i1.2 DOI: https://doi.org/10.4314/sinet.v44i1.2
Gómez Pereira, P., y Mendoza Mora, J. (2004). Guía para la producción de Metarhizium anisopliae. Centro de investigación de la caña de azúcar del Ecuador. CINCAE. https://cincae.org/wp-content/uploads/2013/05/Producci%C3%B3n-Metarhizium-anisopliae-Publicaci%C3%B3n-T%C3%A9cnica-N%C2%B05.pdf
Gómez Ramírez, H., Zapata Granja, A., Torres del Águila, E., y Tenorio Cantoral, M. (2014). Manual de producción y uso de hongos entomopatógenos. SCB-SENASA. Laboratorio de entomopatógenos. https://www.senasa.gob.pe/senasa/wp-content/uploads/2017/09/Manual-de-Producci%C3%83%C2%B3n-y-Uso-de-Hongos-Entomopat%C3%83%C2%B3genos.pdf
Henderson, C. F., y Tilton, E. W. (1955). Tests with Acaricides against the Brown Wheat Mite12. Journal of Economic Entomology, 48(2), 157-161. https://doi.org/10.1093/jee/48.2.157 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/jee/48.2.157
Islam, W., Adnan, M., Shabbir, A., Naveed, H., Abubakar, Y. S., Qasim, M., Tayyab, M., Noman, A., Nisar, M. S., Khan, K. A., y Ali, H. (2021). Insect-fungal-interactions: A detailed review on entomopathogenic fungi pathogenicity to combat insect pests. Microbial Pathogenesis, 159, 105122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micpath.2021.105122 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micpath.2021.105122
Jaber, L. R., y Araj, S.-E. (2018). Interactions among endophytic fungal entomopathogens (Ascomycota: Hypocreales), the green peach aphid Myzus persicae Sulzer (Homoptera: Aphididae), and the aphid endoparasitoid Aphidius colemani Viereck (Hymenoptera: Braconidae). Biological Control, 116, 53-61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocontrol.2017.04.005 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocontrol.2017.04.005
Jing, X., Yuan, Y., Wu, Y., Wu, D., Gong, P., y Gao, M. (2019). Crystal structure of Bacillus thuringiensis Cry7Ca1 toxin active against Locusta migratoria manilensis. Protein Science, 28(3), 609-619. https://doi.org/10.1002/pro.3561 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/pro.3561
Kaczmarek, A., y Boguś, M. I. (2021). Fungi of entomopathogenic potential in Chytridiomycota and Blastocladiomycota, and in fungal allies of the Oomycota and Microsporidia. IMA fungus, 12, 29. https://doi.org/10.1186/s43008-021-00074-y DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s43008-021-00074-y
Kahan, A., Ricci, E., y Hasperué, J. (2002). Comportamiento poblacional de Brevicoryne brassicae L. en tres cultivares de repollo. Revista de Protección Vegetal, 17(3), 225-226. https://agris.fao.org/search/en/records/647246012c1d629bc9796f87
Khan, S., Guo, L., Maimaiti, Y., Mijit, M., y Qiu, D. (2012). Entomopathogenic fungi as microbial biocontrol agent. Molecular Plant Breeding, 3(7), 63-79. https://doi.org/10.5376/mpb.2012.03.0007 DOI: https://doi.org/10.5376/mpb.2012.03.0007
Kim, K.-H., Kabir, E., y Jahan, S. A. (2017). Exposure to pesticides and the associated human health effects. Science of The Total Environment, 575, 525–535. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.09.009 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.09.009
Lacey, L. A. (2017). Chapter 1 - Entomopathogens used as microbial control agents. En L. A. Lacey (ed.), Microbial Control of Insect and Mite Pests (pp. 3-12). Academic Press. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-803527-6.00001-9 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-803527-6.00001-9
Lentini, A., Mannu, R., Cocco, A., Ruio, P. A., Carboneschi, A., y Luciano, P. (2020). Long-term monitoring and microbiological control programs against lepidopteran defoliators in Sardinian cork oak forests (Italy). Annals of Silvicultural Research, 45(1), 21-30. https://doi.org/10.12899/asr-1846
Litwin, A., Nowak, M., y Różalska, S. (2020). Entomopathogenic fungi: unconventional applications. Reviews in Environmental Science and Bio/Technology, 19(1), 23-42. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11157-020-09525-1 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11157-020-09525-1
Mannu, R., Cocco, A., Luciano, P., y Lentini, A. (2020). Influence of Bacillus thuringiensis application timing on population dynamics of gypsy moth in Mediterranean cork oak forests. Pest Management Science, 76(3), 1103-1111. https://doi.org/10.1002/ps.5622 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/ps.5622
Moraes, I. O., Capalbo, D. M. F., y Arruda, R. O. M. (1998). Produção de bactérias entomopatogênicas. En S. B. A. Alves (ed.), Controle microbiano de insetos (2ª ed.) (pp. 815-843). FEALQ. https://www.embrapa.br/busca-de-publicacoes/-/publicacao/12933/producao-de-bacterias-entomopatogenicas
Mukherjee, A., Debnath, P., Ghosh, S. K., y Medda, P. K. (2020). Biological control of papaya aphid (Aphis gossypii Glover) using entomopathogenic fungi. Vegetos, 33(1), 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42535-019-00072-x DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42535-019-00072-x
Murerwa, P., Arama, P. F., Kamau, A. W., y Maniania, N. K. (2014). Effect of infection by Metarhizium anisopliae isolate ICIPE 51 on developmental stage, fecundity, and intrinsic rate of increase of Rhopalosiphum padi and Metopolophium dirhodum. Journal of Entomology and Nematology, 6(11), 154-160. https://doi.org/10.5897/JEN2014. 0114
Mwamburi, L. A. (2021). Endophytic fungi, Beauveria bassiana and Metarhizium anisopliae, confer control of the fall armyworm, Spodoptera frugiperda (JE Smith) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae), in two tomato varieties. Egyptian Journal of Biological Pest Control, 31(1), 1-6. https://doi.org/10.1186/s41938-020-00357-3 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s41938-020-00357-3
Neuwirthová, N., Trojan, M., Svobodová, M., Vašíčková, J., Šimek, Z., Hofman, J., y Bielská, L. (2019). Pesticide residues remaining in soils from previous growing season(s) - Can they accumulate in non-target organisms and contaminate the food web? Science of The Total Environment, 646, 1056-1062. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.07.357 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.07.357
Núñez Seoane, E. (2021). Gestión integrada de plagas en el cultivo de la alfalfa. Agricultura: Revista agropecuaria y ganadera, (1051), 42-46. http://hdl.handle.net/10532/5488
Peña, E., Villazón, L., Jiménez, S., Vázquez, L., y Licor, L. (2000). Alternativas para el control biológico del pulgón pardo de los cítricos (Toxoptera citricidus Kirkaldy) (Homoptera: Aphididae). Fitosanidad, 4(1-2), 75-78. http://www.fitosanidad.cu/index.php/fitosanidad/article/view/213/191
Pohare, M. B., Wagh, S. G., y Udayasuriyan, V. (2021). Bacillus thuringiensis as potential biocontrol agent for sustainable agriculture. En A. N. Yadav, J. Singh, C. Singh, y N. Yadav (eds.), Current Trends in Microbial Biotechnology for Sustainable Agriculture (pp. 439-468). Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-6949-4_18 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-6949-4_18
Quesada-Moraga, E., Landa, B. B., Muñoz-Ledesma, J., Jiménez-Diáz, R. M., y Santiago-Álvarez, C. (2006). Endophytic colonisation of Opium Poppy, Papaver somniferum, by an entomopathogenic Beauveria bassiana strain. Mycopathologia, 161(5), 323-329. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11046-006-0014-0 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11046-006-0014-0
Rao, G., y Narladkar, B. W. (2018). Role of entomopathogenic fungi in tick control: a review. Journal of Entomology and Zoology Studies, 6(1), 1265-1269. https://www.entomoljournal.com/archives/2018/vol6issue1/PartR/6-1-112-205.pdf
Ríos, R., Vargas-Flores, J., Sánchez-Choy, J., Oliva-Paredes, R., Alarcón-Castillo, T., y Villegas, P. (2020). Beauveria bassiana y Metarhizium anisopliae como controladores compatibles y eficientes de insectos plaga en cultivos acuapónicos. Scientia Agropecuaria, 11(3), 419-426. https://doi.org/10.17268/sci.agropecu.2020.03.14 DOI: https://doi.org/10.17268/sci.agropecu.2020.03.14
Russo, M. L., Pelizza, S. A., Cabello, M. N., Stenglein, S. A., y Scorsetti, A. C. (2015). Endophytic colonisation of tobacco, corn, wheat and soybeans by the fungal entomopathogen Beauveria bassiana (Ascomycota, Hypocreales). Biocontrol Science and Technology, 25(4), 475-480. https://doi.org/10.1080/09583157.2014.982511 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/09583157.2014.982511
Silva, C. V. da, Daquila, B. V., Schneider, L. C. L., Caleffe, R. R. T., Polonio, J. C., Canazart, D. A., Nanya, S., y Conte, H. (2021). Potential of Two Metarhizium anisopliae (Clavicipitaceae) Isolates for Biological Control of Diatraea saccharalis (Lepidoptera: Crambidae) Eggs. Advances in Entomology, 10(1), 63-76. https://doi.org/10.4236/ae.2022.101005 DOI: https://doi.org/10.4236/ae.2022.101005
Straw, N. A., y Forster, J. (2022). The effectiveness of ground-based applications of Bacillus thuringiensis var. kurstaki for controlling oak processionary moth Thaumetopoea processionea (Lepidoptera: Thaumetopoeidae). Annals of Applied Biology, 181(1), 48-57. https://doi.org/10.1111/aab.12751 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/aab.12751
Valverde Cadillo, A., Valverde Apfata, N., y Solano Porras, R. (2021). Eficacia del aceite de neem, aceite de eucalipto y caolín en el control biológico de Brevicoryne brassicae. Agroindustrial Science, 11(2), 185-192. https://doi.org/10.17268/agroind.sci.2021.02.08 DOI: https://doi.org/10.17268/agroind.sci.2021.02.08
Villacide, J., y Masciocchi, M. (eds.). (2014). Pulgones. Serie de divulgación sobre insectos de importancia ecológica, económica y sanitaria, No 11. https://inta.gob.ar/sites/default/files/11_-_boletin_pulgones_para_web.pdf
Yari Briones, D. I., Paredes-Valderrama, J. R., Milla Pino, M. E., y Murga Valderrama, N. L. (2021). Efecto del hongo entomopatógeno Beauveria bassiana en el control de garrapatosis en ganado bovino. Revista de Investigaciones Veterinarias del Perú, 32(5), e19586. https://doi.org/10.15381/rivep.v32i5.19586 DOI: https://doi.org/10.15381/rivep.v32i5.19586
Zhang, L., Liu, B., Zheng, W., Liu, C., Zhang, D., Zhao, S., Li, Z., Xu, P., Wilson, K., Withers, A., Jones, C. M., Smith, J. A., Chipabika, G., Kachigamba, D. L., Nam, K., d’Alençon, E., Liu, B., Liang, X., Jin, M., Wu, C., Chakrabarty, S., Yang, X., Jiang, Y., Liu, J., Liu, X., Quan, W., Wang, Fan, G. W., Qian, W., Wu, K., y Xiao, Y. (2020). Genetic structure and insecticide resistance characteristics of fall armyworm populations invading China. Molecular Ecology Resources, 20(6), 1682-1696. https://doi.org/10.1111/1755-0998.13219 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/1755-0998.13219