Endodontic management of a maxillary first premolar with 3 root canal. Case report using cone-beam computed tomography
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.29166/odontologia.vol24.n2.2022-e3940Keywords:
Endodontics, Root Canal therapy, Bicuspid, TomographyAbstract
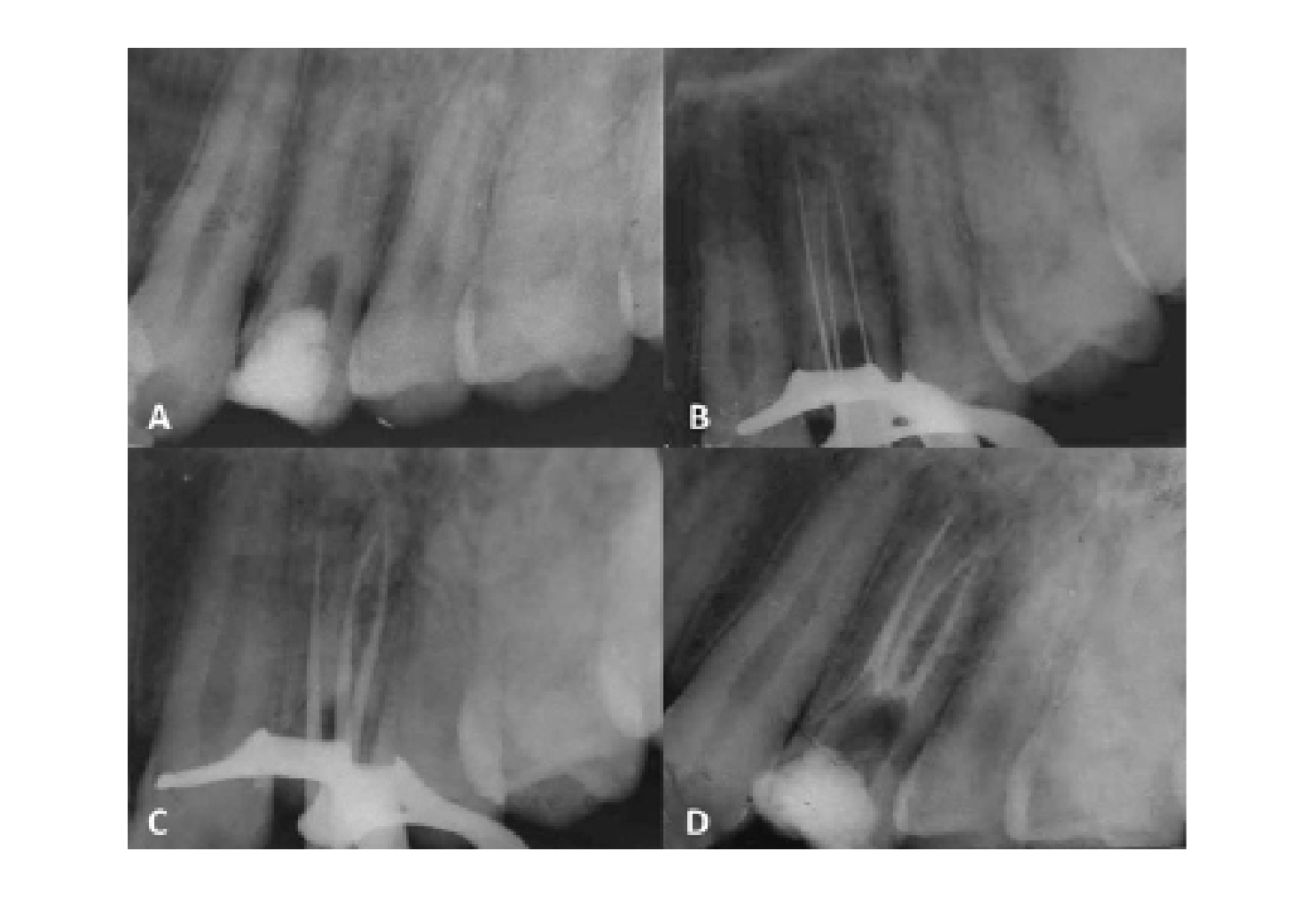
Endodontics is a branch of dentistry, which consists of treating the dental pulp, being important to make a correct diagnosis, collecting all the signs and symptoms. The upper first premolars present anatomical variations and there are probably failures during said therapy due to ignorance of it. According to several studies carried out through radiographs, diaphanizations and computed tomography, the upper first premolars can present three roots and three canals which vary from 0.5 to 6%, this anatomical variant being infrequent. To perform root canal treatment of a maxillary first premolar with 3 canals with the help of computed tomography. An 18-year-old male patient attends the FOUCE clinic for root canal treatment. When performing the intraoral exploration of the right maxillary first premolar, it showed coronal loss, negative thermal tests and positive to the vertical percussion test, in periapical radiography unusual anatomy is shown, computed tomography is performed locating 3 ducts: mesio-vestibular duct, disto-vestibular duct and palatine. Subsequently, the bio-chemo-mechanical preparation was carried out with manual protapper files, final irrigation protocol, thus ending with the obturation with the lateral technique. Thanks to the 3D image of the tomography, the mesio-vestibular, disto-vestibular, and palatal ducts will be detected, preventing a possible perforation due to the morphological complexity of this dental organ. Computed tomography is a test used for anatomical variations of dental organs, avoiding mistakes in the diagnosis and location of canals.Downloads
References
Cobos-Parra D, Moscoso-Abad M. Estudio morfológico de los canales radiculares del primer premolar superior, utilizando radiografía periapical y tomografía de haz cónico, en el centro radiológico dental-maxilofacial, Cuenca 2015. Odontología activa, ucacue. 2016;1(1):56-65.
Canalda C, Brau E. Endodoncia técnicas clinicas y bases cientificas. 3.a ed. Elsevier Health Sciences. 2014;53:309-24.
Kenneth H, Cohen S, Berman L. Cohen, Vías de la pulpa. 10.a ed. México: Elsevier. 2011.
Riojas-Garza MT. Anatomía dental. 2.a ed. Martínez-Moreno M, editor. Anatomía Dental. México, d. f.: Manual Moderno. 2009.
Aznar FDC, Baca-Wiesse PE, Nishiyama CK. Tratamiento endodóntico de un primer premolar superior con 3 raíces: Relato de caso clínico. Acta Odontol. Venez. 2007;45(4):568-71.
Dávila G, Fierro J. Revision bibliografica de la morfología interna de premolares superiores e inferiores. Tesis. Quito: Universidad de las Américas. 2019.
Zaldumbide-Balazero AB. Resolución endodóntica clínica y tomográfica de un primer premolar superior con anatomía dental interna compleja utilizando instrumentación mecanizada. Reporte de caso clínico. Facultad de Ciencias Médicas, de la Salud y de la Vida, Escuela de Odontologia. Universidad Internacional del Ecuador. 2019.
De la Rosa-Fernandéz K, Farfán-Chacha A. Estudio de la prevalencia de un tercer conducto en primeros premolares superiores mediante diafanización Rev Odontología. 2016;18(1):26-32.
Plascencia H, Ortiz D, Gascón G, Cruz Á, Díaz M. Manejo endodóntico de un primer premolar maxilar con tres raíces. Rev Asoc Odontol Argent. 2014;102(3):126-9.
Vertucci FJ, Gegauff A. Root canal morphology of the maxillary first premolar. J Am Dent Assoc. 1979;99(2):194-8.
Ahmad IA, Alenezi MA. Root and root canal morphology of maxillary first premolars: a literature review and clinical considerations. J Endod. 2016;42(6):861-72.
Bürklein S, Heck R, Schäfer E. Evaluation of the root canal anatomy of maxillary and mandibular premolars in a selected german population using cone-beam computed tomographic data. J Endod. 2017;43(9):1448-52.
Tobares MGC, Carranza TMF. Corona AGL, Peña RD. Preparación biomecánica ideal de primeros premolares maxilares con anatomía complicada. Oral. 2017;17(53):1310-5.
Sierra LG, Gualtieri A, Cuadros MV, Labarta, AB. Evaluación de la morfología radicular interna de premolares inferiores mediante la técnica de diafanización, obtenidos de una población argentina. Revista Científica Odontológica [Internet]. 2016;12(1):19-27. https://www.redalyc.org/articulo.oa?id=324248526004
Corona-Tabares MG, Barajas-Cortez L, Villegas-Medina O, Quiñónez-Zárate LA, Gutiérrez-Dueñas I. Manual de endodoncia básica. México: Ecorfan. 2014.
Moreano Granizo SA, Vallejo Lara SV, Cárdenas Guamán SV, Silva Tapia GC. Anatomía interna del primer premolar superior mediante la técnica de diafanización [Internet]. 2021. http://dx.doi.org/10.23857/pc.v6i1.2144
Garofletti J, Luján G. Tratamiento endodóntico total en premolar superior [Internet]. 2014. Disponible en: https://rdu.unc.edu.ar/bitstream/handle/11086/15796/Tratamiento%20endod%C3%B3ntico%20total%20en%20premolar%20superior.pdf?sequence=3&isAllowed=y
Fernández R, Cardona JA. Anatomía radicular, una mirada desde la micro-cirugía endodóntica: Revisión. Revista ces Odontología [Internet]. 2015;n 28:30. Disponible en: http://dx.doi.org/0120-971X
Oporto G, Fuentes R, Soto C. Variaciones anatómicas radiculares y sistemas de canales. Scielo. 2010;6.
Moreano-Granizo S. Estudio in-vitro de la anatomía interna de conductos radiculares del primer premolar superior, estudio mediante la técnica de diafanización dental. [Ecuador]: Universidad Nacional de Chimborazo. 2018.
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.

