Biodegradación de pesticidas por microorganismos aislados de compost
Contenido principal del artículo
Resumen
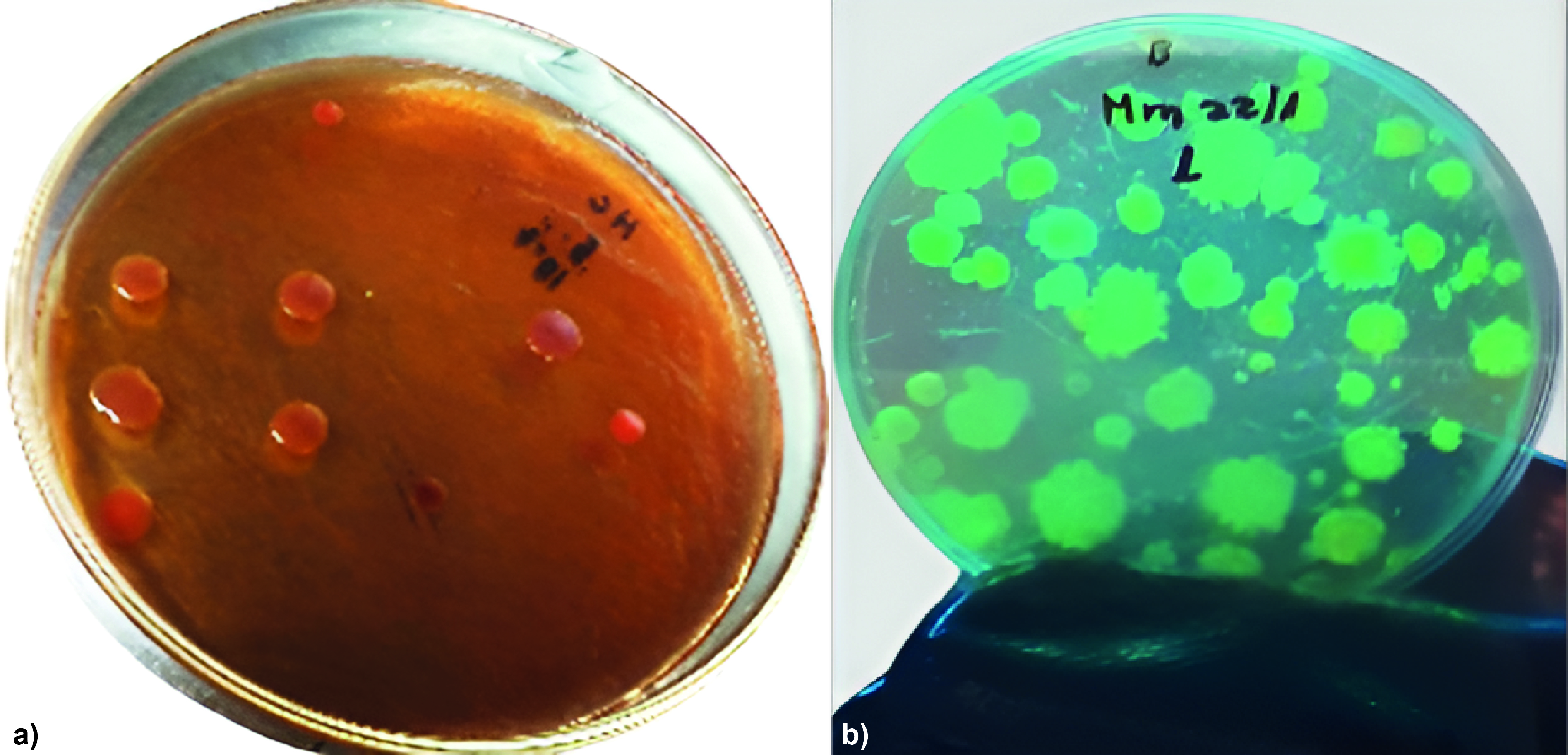
La degradación del suelo y la baja productividad agrícola a menudo se han relacionado con el uso indiscriminado de pesticidas. En los últimos años, con el objetivo de restaurar la fertilidad del suelo, los agricultores han recurrido al uso de fertilizantes orgánicos, los cuales aportan tanto macronutrientes como micronutrientes para mejorar la producción agrícola. Sin embargo, la carga microbiana de estos fertilizantes también puede afectar a las poblaciones biológicas del suelo, su diversidad y su actividad. En este contexto, los objetivos de este estudio fueron evaluar la calidad microbiológica de muestras de compost y realizar pruebas de degradación de pesticidas. Los análisis microbiológicos revelaron que la carga microbiana del compost estaba compuesta principalmente por hongos fitopatógenos, como Fusarium spp. y Cladosporium spp., así como por bacterias fitopatógenas, incluidas Pseudomonas spp. y enterobacterias, las cuales pueden ser patógenas para humanos y animales. La población y diversidad de actinomicetos fue notablemente baja. Análisis previos identificaron la persistencia de pesticidas como glifosato, clorfenapir y difenoconazol en las muestras. Las bacterias y actinomicetos más abundantes, caracterizados como Pseudomonas spp. y Streptomyces spp. (ACP1 y ACP2), fueron eficaces en la degradación de estos plaguicidas en condiciones in vitro. Específicamente, el difenoconazol se degradó hasta en un 70 %, el clorfenapir en un 44 % y el glifosato en un 30 %, tanto de forma individual como en mezclas, reduciendo así la concentración de estos contaminantes y demostrando el potencial de estos microorganismos en procesos de descontaminación y biorremediación.
Descargas
Métricas
Detalles del artículo

Esta obra está bajo una licencia internacional Creative Commons Atribución-NoComercial 4.0.
Los autores que publican en Siembra conocen y aceptan las siguientes condiciones:
- Los autores retienen los derechos de copia (copyright) y ceden a Siembra el derecho de primera publicación del trabajo, bajo licencia Creative Commons Attribution License, que permite a terceros utilizar lo publicado siempre que hagan referencia al autor o autores del trabajo y a su publicación en esta revista.
![]() Esta obra está bajo una Licencia Creative Commons Reconocimiento-NoComercial 4.0 Internacional (CC BY-NC 4.0).
Esta obra está bajo una Licencia Creative Commons Reconocimiento-NoComercial 4.0 Internacional (CC BY-NC 4.0).
- Los autores conservan los derechos de autor y garantizan a Siembra el derecho de publicar el manuscrito a través de los canales que considere adecuados.
- Los autores pueden establecer por su cuenta acuerdos adicionales para la distribución no exclusiva de la versión de la obra publicada en Siembra, haciendo reconocimiento de su publicación inicial en la misma, como por ejemplo en repositorios institucionales.
Se autoriza a los autores a difundir sus trabajos electrónicamente una vez sea aceptado el manuscrito para su publicación.
Citas
Agu, K. C., & Chidozie, C. P. (2021). An improved slide culture technique for the microscopic identification of fungal species. International Journal of Trend in Scientific Research and Development, 6(1), 243-254. https://www.ijtsrd.com/papers/ijtsrd45058.pdf
Ahamad, A., & Kumar, J. (2023). Pyrethroid pesticides: An overview on classification, toxicological assessment and monitoring. Journal of Hazardous Materials Advances, 10, 100284. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hazadv.2023.100284 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hazadv.2023.100284
Ahmad, K. S. (2020). Remedial potential of bacterial and fungal strains (Bacillus subtilis, Aspergillus niger, Aspergillus flavus and Penicillium chrysogenum) against organochlorine insecticide Endosulfan. Folia microbiologica, 65(5), 801-810. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12223-020-00792-7 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12223-020-00792-7
Ahmad, S., Ahmad, H. W., & Bhatt, P. (2022). Microbial adaptation and impact into the pesticide’s degradation. Archives of Microbiology, 204(5), 288. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-022-02899-6 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-022-02899-6
Akyol, Ç., Ince, O., & Ince, B. (2019). Crop-based composting of lignocellulosic digestates: Focus on bacterial and fungal diversity. Bioresource technology, 288, 121549. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2019.121549 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2019.121549
Ameen, F., & Al-Homaidan, A. A. (2020). Compost inoculated with fungi from a mangrove habitat improved the growth and disease defense of vegetable plants. Sustainability, 13(1), 124. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13010124 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/su13010124
An, Y. Q., Dong, Y. L., Hao, S. N., Xiao, H., Tian, Y. P., & Gong, Y. (2024). Survival after chlorfenapyr intoxication by non-gastrointestinal route. Clinical Toxicology, 62(2), 134-135. https://doi.org/10.1080/15563650.2024.2310748 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/15563650.2024.2310748
Araujo, R. (2022). Advances in soil engineering: sustainable strategies for rhizosphere and bulk soil microbiome enrichment. Frontiers in Bioscience-Landmark, 27(6), 195. https://doi.org/10.31083/j.fbl2706195 DOI: https://doi.org/10.31083/j.fbl2706195
Ayed, F., Abdallah, R. A. B., Jabnoun-Khiareddine, H., & Daami-Remadi, M. (2021). Selection of compost-derived actinomycetes with plant-growth promoting and tomato stem rot biocontrol potentialities. Journal of Phytopathology and Disease Management, 8(1), 79-91. https://core.ac.uk/download/483700402.pdf
Bamdad, H., Papari, S., Lazarovits, G., & Berruti, F. (2022). Soil amendments for sustainable agriculture: Microbial organic fertilizers. Soil Use and Management, 38(1), 94-120. https://doi.org/10.1111/sum.12762 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/sum.12762
Bhimani, A. A., Bhimani, H. D., Vaghela, N. R., & Gohel, S. D. (2024). Cultivation methods, characterization, and biocatalytic potential of organic solid waste degrading bacteria isolated from sugarcane rhizospheric soil and compost. Biologia, 79(3), 953-974. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11756-023-01592-3 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11756-023-01592-3
Boiu-Sicuia, O.-A., Stan, V., & Cornea, C. P. (2021). The compost, a source of plant beneficial bacteria with biocontrol potential. Current Trends in Natural Sciences, 10(20), 32-38. https://doi.org/10.47068/ctns.2021.v10i20.004 DOI: https://doi.org/10.47068/ctns.2021.v10i20.004
Buol, S. W., Southard, R. J., Graham, R. C., & McDaniel, P. A. (2011). Soil Genesis and Classification. Wiley. https://doi.org/10.1002/9780470960622 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/9780470960622
Buzón-Durán, L., Pérez-Lebeña, E., Martín-Gil, J., Sánchez-Báscones, M., & Martín-Ramos, P. (2020). Applications of Streptomyces spp. Enhanced Compost in Sustainable Agriculture. In M. Meghvansi & A. Varma (eds.), Biology of Composts. Soil Biology (Vol. 58, pp. 257-291). Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-39173-7_13 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-39173-7_13
Carpio, M. J., Sánchez-Martín, M. J., Rodríguez-Cruz, M. S., & Marín-Benito, J. M. (2021). Effect of organic residues on pesticide behavior in soils: a review of laboratory research. Environments, 8(4), 32. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments8040032 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/environments8040032
Castrejón-Godínez, M. L., Tovar-Sánchez, E., Valencia-Cuevas, L., Rosas-Ramírez, M. E., Rodríguez, A., & Mussali-Galante, P. (2021). Glyphosate pollution treatment and microbial degradation alternatives, a review. Microorganisms, 9(11), 2322. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9112322 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9112322
Chen, L., Zhang, H., Jia, X., Fang, Y., & Lin, C. (2024). Soil fertility and bacterial community composition in response to the composting of biochar-amended chicken manure. Agronomy, 14(5), 886. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14050886 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14050886
Cheng, M., Chen, D., Parales, R. E., & Jiang, J. (2022). Oxygenases as powerful weapons in the microbial degradation of pesticides. Annual Review of Microbiology, 76(1), 325-348. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-micro-041320-091758 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-micro-041320-091758
Chopkova, V., Petkova, M., & Shilev, S. (2023). Uncovering bacterial diversity during mesophilic and thermophilic phases of biowaste composting through next-generation sequencing. Applied Sciences, 13(5), 3111. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13053111 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/app13053111
Chorolque, A., Pellejero, G., Sosa, M. C., Palacios, J., Aschkar, G., García-Delgado, C., & Jiménez-Ballesta, R. (2021). Biological control of soil-borne phytopathogenic fungi through onion waste composting: implications for circular economy perspective. International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 19(7), 6411-6420. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-021-03561-2 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-021-03561-2
Conde-Avila, V., Ortega-Martínez, L. D., Loera, O., el Kassis, E. G., Dávila, J. G., Valenzuela, C. M., & Armendáriz, B. P. (2021). Pesticides degradation by immobilised microorganisms. International Journal of Environmental Analytical Chemistry, 101(15), 2975-3005. https://doi.org/10.1080/03067319.2020.1715375 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/03067319.2020.1715375
Correa, L. O., Bezerra, A. F. M., Honorato, L. R. S., Cortêz, A. C. A., Souza, J. V. B., & Souza, E. S. (2021). Amazonian soil fungi are efficient degraders of glyphosate herbicide; novel isolates of Penicillium, Aspergillus, and Trichoderma. Brazilian Journal of Biology, 83, e242830. https://doi.org/10.1590/1519-6984.242830 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1590/1519-6984.242830
Ćwiertniewicz-Wojciechowska, M., Ślipko, K., Banach-Wiśniewska, A., & Ziembińska-Buczyńska, A. (2023). Influence of the autochthonous cellulolytic bacteria on the domestic compost process improvement. BioTechnologia, 104(1), 5-20. https://doi.org/10.5114/bta.2023.125082 DOI: https://doi.org/10.5114/bta.2023.125082
Danish, S. A., Haq, T., Liaqat, I., Rubab, S., Qureshi, M., & Zafar, U. (2021). Succession and Catabolic Properties of Fungal Community During Composting of Fruit Waste at Sub-Tropical Environment. https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-704507/v1 DOI: https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-704507/v1
Dar, M. A., Shahnawaz, M., Hussain, K., Gupta, P., Sirwal, M. Y., Sadaqat, B., Gazal, S., Akhtar, R., Parihar, S., Zhu, D., Adetunji, C. O., Fardos, T., Parihar, J., Omorefosa, O. O., Xie, R., & Sun, J. (2023). Natural compounds for bioremediation and biodegradation of pesticides. In S. N. Meena, V. Nandre, K. Kodam, & R. S. Meena (eds.), New Horizons in Natural Compound Research (pp. 445-488). Academic Press. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-443-15232-0.00015-1 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-443-15232-0.00015-1
Das, P., Singh, S. K., Singh, P., Zeyad, M. T., Aamir, M., & Upadhyay, R. S. (2021). Actinomycetes as biostimulants and their application in agricultural practices. In J. White, A. Kumar, & S. Droby (eds.), Microbiome stimulants for crops (pp. 267-282). Woodhead Publishing. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-822122-8.00021-2 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-822122-8.00021-2
de Corato, U. (2020). Disease-suppressive compost enhances natural soil suppressiveness against soil-borne plant pathogens: A critical review. Rhizosphere, 13, 100192. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rhisph.2020.100192 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rhisph.2020.100192
de Sousa, T., Hébraud, M., Dapkevicius, M. L. N. E., Maltez, L., Pereira, J. E., Capita, R., Alonso-Calleja, C., Igrejas, G., & Poeta, P. (2021). Genomic and metabolic characteristics of the pathogenicity in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(23), 12892. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222312892 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222312892
Durán-Lara, E. F., Valderrama, A., & Marican, A. (2020). Natural organic compounds for application in organic farming. Agriculture, 10(2), 41. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture10020041 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture10020041
Esikova, T. Z., Anokhina, T. O., Suzina, N. E., Shushkova, T. V., Wu, Y., & Solyanikova, I. P. (2023). Characterization of a new Pseudomonas putida strain Ch2, a degrader of toxic anthropogenic compounds epsilon-caprolactam and glyphosate. Microorganisms, 11(3), 650. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11030650 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11030650
Esimbekova, E. N., Kalyabina, V. P., Kopylova, K. v., Lonshakova-Mukina, V. I., Antashkevich, A. A., Torgashina, I. G., Lukyanenko, K. A., & Kratasyuk, V. A. (2022). The effects of commercial pesticide formulations on the function of in vitro and in vivo assay systems: A comparative analysis. Chemosensors, 10(8), 328. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors10080328 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors10080328
Esparza-Naranjo, S. B., da Silva, G. F., Duque-Castaño, D. C., Araújo, W. L., Peres, C. K., Boroski, M., & Bonugli-Santos, R. C. (2021). Potential for the biodegradation of atrazine using leaf litter fungi from a subtropical protection area. Current Microbiology, 78, 358-368. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-020-02288-6 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-020-02288-6
Fauriah, R., Amin, N., Daud, I. D., & Harsanti, E. S. (2021). The potential of endophytic fungi as biodegradation of chlorpyrifos in shallots. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, 807(3), 032058. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/807/3/032058 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/807/3/032058
Fischer, G., & Dott, W. (2002). Quality assurance and good laboratory practice in the mycological laboratory – compilation of basic techniques for the identification of fungi. International Journal of Hygiene and Environmental Health, 205(6), 433-442. https://doi.org/10.1078/1438-4639-00190 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1078/1438-4639-00190
Fuchs, B., Laihonen, M., Muola, A., Saikkonen, K., Dobrev, P. I., Vankova, R., & Helander, M. (2022). A glyphosate-based herbicide in soil differentially affects hormonal homeostasis and performance of non-target crop plants. Frontiers in Plant Science, 12, 787958. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2021.787958 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2021.787958
Girard, L., Lood, C., Höfte, M., Vandamme, P., Rokni-Zadeh, H., van Noort, V., Lavigne, R., & de Mot, R. (2021). The ever-expanding pseudomonas genus: description of 43 new species and partition of the Pseudomonas putida group. Microorganisms, 9(8), 1766. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9081766 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9081766
Grgas, D., Rukavina, M., Bešlo, D., Štefanac, T., Crnek, V., Šikić, T., Habuda-Stanić, M., & Landeka Dragičević, T. (2023). The Bacterial Degradation of Lignin—A Review. Water, 15(7), 1272. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15071272 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/w15071272
Grigorova-Pesheva, B., Malcheva, B., & Peshev, a. (2024). Microbial community dynamics of compost mixtures after application of microbiological additive. Scientific Papers. Series A. Agronomy, 67(1), 1. https://www.agronomyjournal.usamv.ro/index.php/scientific-papers/current?id=1723
Guerrero Ramírez, J. R., Ibarra Muñoz, L. A., Balagurusamy, N., Frías Ramírez, J. E., Alfaro Hernández, L., & Carrillo Campos, J. (2023). Microbiology and Biochemistry of Pesticides Biodegradation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(21), 15969. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242115969 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242115969
Harrigan, W. F., & McCance, M. E. (2014). Laboratory methods in microbiology. Academic press.
Hernández-Mesa, M., & Moreno-González, D. (2022). Current role of mass spectrometry in the determination of pesticide residues in food. Separations, 9(6), 148. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations9060148 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/separations9060148
Huang, P., Yan, X., Yu, B., He, X., Lu, L., & Ren, Y. (2023). A comprehensive review of the current knowledge of chlorfenapyr: synthesis, mode of action, resistance, and environmental toxicology. Molecules, 28(22), 7673. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28227673 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28227673
Ibrahim, I. A. J., & Hameed, T. A. K. (2015). Isolation, characterization and antimicrobial resistance patterns of lactose-fermenter enterobacteriaceae isolates from clinical and environmental samples. Open Journal of Medical Microbiology, 5(04), 169-176. http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/ojmm.2015.54021 DOI: https://doi.org/10.4236/ojmm.2015.54021
Jakubus, M., & Michalak-Oparowska, W. (2022). Valorization of quality of vermicomposts and composts using various parameters. Agriculture, 12(2), 293. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture12020293 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture12020293
Jeong, D. K., Lee, H. J., Bae, J. Y., Jang, Y. S., Hong, S. M., & Kim, J. H. (2019). Chlorfenapyr residue in sweet persimmon from farm to table. Journal of food protection, 82(5), 810-814. https://doi.org/10.4315/0362-028X.JFP-18-503 DOI: https://doi.org/10.4315/0362-028X.JFP-18-503
Kannan, R., & Kallapiran, K. A. (2022). A Review on the Agricultural Waste Residues Management by Different Microbes. Journal of Agriculture and Ecology Research International, 23(6), 93-113. https://doi.org/10.9734/jaeri/2022/v23i6502 DOI: https://doi.org/10.9734/jaeri/2022/v23i6502
Khazal, S. S., & Suhail, F. M. (2022). Study of the analysis of microbial dusting pesticides caused by Pseudomonas bacteria and Trichoderma fungi. International Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 7(2), 1755-1315. https://kalaharijournals.com/resources/FebV7_I2_375%20(1).pdf
Kraut-Cohen, J., Zolti, A., Rotbart, N., Bar-Tal, A., Laor, Y., Medina, S., Shawahna, R., Saadi, I., Raviv, M., Green, S. J., Yermiyahu, U., & Minz, D. (2023). Short- and long-term effects of continuous compost amendment on soil microbiome community. Computational and Structural Biotechnology Journal, 21, 3280-3292. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.csbj.2023.05.030 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.csbj.2023.05.030
Kumar, R. R., & Jadeja, V. J. (2016). Isolation of Actinomycetes: A Complete Approach. International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences, 5(5), 606-618. https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2016.505.062 DOI: https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2016.505.062
Kunanbayev, K., Churkinа, G., Rukavitsina, I., Filippova, N., & Utebayev, M. (2019). Potential attractiveness of soil fungus Trichoderma inhamatum for biodegradation of the glyphosate herbicide. Journal of Ecological Engineering, 20(11), 240-245. https://doi.org/10.12911/22998993/113580 DOI: https://doi.org/10.12911/22998993/113580
Kurakov, A. V., & Bilanenko, E. N. (2023). Dynamics of mycobiota during composting of cow manure and straw. Eurasian Soil Science, 56(4), 453-469. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1064229322602554 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1064229322602554
Lakshmanan, R., Kalaimurugan, D., Sivasankar, P., Arokiyaraj, S., & Venkatesan, S. (2020). Identification and characterization of Pseudomonas aeruginosa derived bacteriocin for industrial applications. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 165, 2412-2418. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.10.126 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.10.126
Lau, Y. Y., Hernandes, E., Kristanti, R. A., Wijayanti, Y., & Emre, M. (2023). Exploring the potential of composting for bioremediation of pesticides in agricultural sector. Industrial and Domestic Waste Management, 3(1), 47-66. https://doi.org/10.53623/idwm.v3i1.245 DOI: https://doi.org/10.53623/idwm.v3i1.245
Leskovac, A., & Petrović, S. (2023). Pesticide use and degradation strategies: food safety, challenges and perspectives. Foods, 12(14), 2709. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12142709 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12142709
Liu, F., Wang, Y., Chen, L., Bello, B. K., Zhang, T., Yang, H., Li, X., Pan, E., Feng, H., & Dong, J. (2022). Difenoconazole disrupts the blood-brain barrier and results in neurotoxicity in carp by inhibiting the Nrf2 pathway mediated ROS accumulation. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 244, 114081. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2022.114081 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2022.114081
Liu, G., Yang, Y., Ma, R., Jiang, J., Li, G., Wang, J., Wuyun, D., & Yuan, J. (2023). Thermophilic compost inoculating promoted the maturity and mature compost inoculating reduced the gaseous emissions during co-composting of kitchen waste and pig manure. Environmental Technology & Innovation, 32, 103427. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eti.2023.103427 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eti.2023.103427
Liu, Y., Cheng, D., Xue, J., Weaver, L., Wakelin, S. A., Feng, Y., & Li, Z. (2020). Changes in microbial community structure during pig manure composting and its relationship to the fate of antibiotics and antibiotic resistance genes. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 389, 122082. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.122082 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.122082
Lv, Z., Tao, C., Zhang, J., Shen, Z., Wang, D., Wang, B., Liu, H., & Li, R. (2023). Moderately delayed maturation of composting promotes the reduction of guild-plant pathogenic fungi within vegetable waste. Research Square. https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-3032959/v1 DOI: https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-3032959/v1
Maleki, M., Mostafaee, S., Mokhtarnejad, L., & Farzaneh, M. (2010). Characterization of Pseudomonas fluorescens strain CV6 isolated from cucumber rhizosphere in Varamin as a potential biocontrol agent. Australian Journal of Crop Science, 4(9), 676-683. https://www.cropj.com/maleki_4_9_2010_676_683.pdf
Man, Y., Stenrød, M., Wu, C., Almvik, M., Holten, R., Clarke, J. L., Yuan, S., Wu, X., Xu, J., Dong, F., Zheng, Y., & Liu, X. (2021). Degradation of difenoconazole in water and soil: Kinetics, degradation pathways, transformation products identification and ecotoxicity assessment. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 418, 126303. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.126303 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.126303
Mashi, B. H. (2018). Antibiotic Susceptibility Patterns of Pseudomonas spp. Isolated from Soil Samples. UMYU Journal of Microbiology Research (UJMR), 3(2), 27-31. https://doi.org/10.47430/ujmr.1832.005 DOI: https://doi.org/10.47430/ujmr.1832.005
Matúš, P., Littera, P., Farkas, B., & Urík, M. (2023). Review on performance of Aspergillus and Penicillium species in biodegradation of organochlorine and organophosphorus pesticides. Microorganisms, 11(6), 1485. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11061485 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11061485
Mehta, J. S., & Jadeja, B. A. (2022). Biochemical and physiological characterization of actinomycetes isolated from rhizospheric regions in the soils of Arachis hypogea L. and Gossypium herbaceum L. near the Gir Wildlife Sanctuary. Journal of Pharmaceutical Negative Results, 13(8), 267-273. https://doi.org/10.47750/pnr.2022.13.S08.40 DOI: https://doi.org/10.47750/pnr.2022.13.S08.40
Meng, Q., Yang, W., Men, M., Bello, A., Xu, X., Xu, B., Deng, L., Jiang, X., Sheng, S., Wu, X., Han, Y., & Zhu, H. (2019). Microbial community succession and response to environmental variables during cow manure and corn straw composting. Frontiers in Microbiology, 10, 529. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2019.00529 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2019.00529
Midhat, M. S., & Abed, S. M. (2023). Isolation and identification of pathogenic species of the genus Pseudomonas and study of antibiotic resistance. GSC Biological and Pharmaceutical Sciences, 23(1), 087-098. https://doi.org/10.30574/gscbps.2023.23.1.0144 DOI: https://doi.org/10.30574/gscbps.2023.23.1.0144
Mohammad, A. O., Alkurtany, A. E., & Hassan, A. A. (2020). Evaluation of API 20E system in fluorescent Pseudomonas identification from button mushroom Agaricus bisporus cultivation casing soil. Notulae Scientia Biologicae, 12(2), 258-263. http://dx.doi.org/10.15835/nsb12210628 DOI: https://doi.org/10.15835/nsb12210628
Mohapatra, D., Rath, S. K., & Mohapatra, P. K. (2022). Soil fungi for bioremediation of pesticide toxicants: A perspective. Geomicrobiology Journal, 39(3-5), 352-372. https://doi.org/10.1080/01490451.2021.2019855 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/01490451.2021.2019855
Mustapha, M. U., Halimoon, N., Johar, W. L. W., & Abd Shukor, M. Y. (2019). An overview on biodegradation of carbamate pesticides by soil bacteria. Pertanika Journal of Science & Technology, 27(2), 547-563. http://psasir.upm.edu.my/id/eprint/68692/
Naeem, U., Afzaal, M., Haq, I. ul, Qazi, A., Naeem, A., & Mahfooz, Y. (2022). A Comparative Role of Competent Microbes for Value-added Composting of Agricultural Waste. Research Square. https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-2087247/v1 DOI: https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-2087247/v1
Narsing Rao, M. P., & Li, W. J. (2022). Diversity of Actinobacteria in various habitats. In L. Karthik (ed.), Actinobacteria: Microbiology to Synthetic Biology (pp. 37-58). Springer Nature Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-5835-8. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-5835-8_2 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-5835-8_2
Nazari, M. T., Machado, B. S., Marchezi, G., Crestani, L., Ferrari, V., Colla, L. M., & Piccin, J. S. (2022). Use of soil actinomycetes for pharmaceutical, food, agricultural, and environmental purposes. 3 Biotech, 12(9), 232. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-022-03307-y DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-022-03307-y
Nazem Shirazi, M. H., Soltani Majd, N., & Khodayari, M. (2023). Molecular and Biochemical Characterization of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Isolated from a Turkey Flock. Journal of Poultry Sciences and Avian Diseases, 1(2), 42-46. https://doi.org/10.61838/kman.jpsad.1.2.6 DOI: https://doi.org/10.61838/kman.jpsad.1.2.6
O'hara, C. M. (2005). Manual and automated instrumentation for identification of Enterobacteriaceae and other aerobic gram-negative bacilli. Clinical microbiology reviews, 18(1), 147-162. https://doi.org/10.1128/cmr.18.1.147-162.2005 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1128/CMR.18.1.147-162.2005
Oyedoh, O. P., Yang, W., Dhanasekaran, D., Santoyo, G., Glick, B. R., & Babalola, O. O. (2023). Rare rhizo-Actinomycetes: A new source of agroactive metabolites. Biotechnology Advances, 67, 108205. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2023.108205 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2023.108205
Palaniveloo, K., Amran, M. A., Norhashim, N. A., Mohamad-Fauzi, N., Peng-Hui, F., Hui-Wen, L., Kai-Lin, Y., Jiale, L., Chian-Yee, M. G., Jing-Yi, L., Gunasekaran, B., & Razak, S. A. (2020). Food Waste Composting and Microbial Community Structure Profiling. Processes, 8(6), 723. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8060723 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8060723
Pant, R., Tiwari, K., Singh, A., Srivastava, S., Patrick, N., & Gupta, A. (2022). Screening, Isolation and characterization of Soil microbes at the banks of the Song River. Bulletin of Environment, Pharmacology and Life Sciences, 12(1), 141-148. https://bepls.com/dec_2022/20.pdf
Parra-Arroyo, L., González-González, R. B., Castillo-Zacarías, C., Melchor Martínez, E. M., Sosa-Hernández, J. E., Bilal, M., Iqbal, H. M. N., Barceló, D., & Parra-Saldívar, R. (2022). Highly hazardous pesticides and related pollutants: Toxicological, regulatory, and analytical aspects. Science of The Total Environment, 807, 151879. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.151879 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.151879
Peillex, C., & Pelletier, M. (2020). The impact and toxicity of glyphosate and glyphosate-based herbicides on health and immunity. Journal of immunotoxicology, 17(1), 163-174. https://doi.org/10.1080/1547691X.2020.1804492 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/1547691X.2020.1804492
Pérez-Corral, D. A., Ornelas-Paz, J. de J., Olivas-Orozco, G. I., Acosta-Muñiz, C. H., Salas-Marina, M. Á., Berlanga-Reyes, D. I., Ruiz-Cisneros, M. F., & Rios-Velasco, C. (2022). Molecular, morphological and biochemical characterization of actinomycetes and their antagonistic activity against phytopathogenic fungi. Revista Fitotecnia Mexicana, 45(1), 103. https://doi.org/10.35196/rfm.2022.1.103 DOI: https://doi.org/10.35196/rfm.2022.1.103
Pizzul, L., Castillo, M. D. P., & Stenström, J. (2009). Degradation of glyphosate and other pesticides by ligninolytic enzymes. Biodegradation, 20, 751-759. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-009-9263-1 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-009-9263-1
Qin, G., Chen, Y., He, F., Yang, B., Zou, K., Shen, N., Zuo, B., Liu, R., Zhang, W., & Li, Y. (2021). Risk assessment of fungicide pesticide residues in vegetables and fruits in the mid-western region of China. Journal of Food Composition and Analysis, 95, 103663. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfca.2020.103663 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfca.2020.103663
Raffa, C. M., & Chiampo, F. (2021). Bioremediation of agricultural soils polluted with pesticides: A review. Bioengineering, 8(7), 92. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering8070092 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering8070092
Rafieenia, R., Mahmoud, M., El-Gohary, F., & Rossa, C. A. (2022). The degradation of glyphosate is enhanced in a microbial fuel cell: Electrochemical performance, degradation efficiency, and analysis of the anodic microbial community. Sustainable Energy Technologies and Assessments, 54, 102805. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seta.2022.102805 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seta.2022.102805
Randika, J. L. P. C., Bandara, P. K. G. S. S., Soysa, H. S. M., Ruwandeepika, H. A. D., & Gunatilake, S. K. (2022). Bioremediation of pesticide-contaminated soil: a review on indispensable role of soil bacteria. Journal of Agricultural Sciences – Sri Lanka, 17(1), 19-43. https://doi.org/10.4038/jas.v17i1.9609 DOI: https://doi.org/10.4038/jas.v17i1.9609
Rasool, S., Rasool, T., & Gani, K. M. (2022). A review of interactions of pesticides within various interfaces of intrinsic and organic residue amended soil environment. Chemical Engineering Journal Advances, 11, 100301. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceja.2022.100301 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceja.2022.100301
Rastogi, M., Nandal, M., & Khosla, B. (2020). Microbes as vital additives for solid waste composting. Heliyon, 6(2), e03343. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e03343 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e03343
Riedo, J., Wächter, D., Gubler, A., Wettstein, F. E., Meuli, R. G., & Bucheli, T. D. (2023). Pesticide residues in agricultural soils in light of their on-farm application history. Environmental Pollution, 331, 121892. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2023.121892 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2023.121892
Rigolin, F. R., Leite, C. A., Birolli, W. G., Porto, A. L., & Seleghim, M. H. (2024). Biodegradation of the pyrethroid pesticide gamma-cyhalothrin by fungi from a Brazilian cave. Journal of the Brazilian Chemical Society, 35, e-20240026. https://dx.doi.org/10.21577/0103-5053.20240026 DOI: https://doi.org/10.21577/0103-5053.20240026
Rodríguez, A., Castrejón-Godínez, M. L., Salazar-Bustamante, E., Gama-Martínez, Y., Sánchez-Salinas, E., Mussali-Galante, P., Tovar-Sánchez, E., & Ortiz-Hernández, Ma. L. (2020). Omics Approaches to Pesticide Biodegradation. Current Microbiology, 77(4), 545–563. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-020-01916-5 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-020-01916-5
Rodríguez, C. A., Gavilánez, T. C., Chamorro, J. P., Vinueza, A. G., Salazar, D. M., & Arancibia, M. Y. (2018). Selective Isolation and Phenotypic Characterization of Bacteria and Actinomycetes from Oil-contaminated Soils. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, 151, 012039. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/151/1/012039 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/151/1/012039
Rodríguez-Fonseca, M. F., Sánchez-Suárez, J., Valero, M. F., Ruiz-Balaguera, S., & Díaz, L. E. (2021). Streptomyces as potential synthetic polymer degraders: A systematic review. Bioengineering, 8(11), 154. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering8110154 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering8110154
Rossi, F., Carles, L., Donnadieu, F., Batisson, I., & Artigas, J. (2021). Glyphosate-degrading behavior of five bacterial strains isolated from stream biofilms. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 420, 126651. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.126651 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.126651
Ruiz-Hernandez, I. H., Madrigal-Perez, L. A., & González-Hernández, J. C. (2024). The potential use of Pseudomonas in terrestrial and space agriculture. Brazilian Journal of Biology, 84. https://doi.org/10.1590/1519-6984.282664 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1590/1519-6984.282664
Ruomeng, B., Meihao, O., Siru, Z., Shichen, G., Yixian, Z., Junhong, C., Ruijie, M., Yuan, L., Gezhi, X., Xingyu, C., Shiyi, Z., Aihui, Z., & Baishan, F. (2023). Degradation strategies of pesticide residue: From chemicals to synthetic biology. Synthetic and Systems Biotechnology, 8(2), 302-313. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.synbio.2023.03.005 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.synbio.2023.03.005
Salazar Calvo, C., Moya García, A., González Venegas, J. P., Rodríguez Díaz, H., & Corrales Valverde, D. (2020). Comparación de dos métodos de muestreo para el análisis de fertilidad de suelos. Alcances Tecnológicos, 13(1), 31–39. https://doi.org/10.35486/at.v13i1.168 DOI: https://doi.org/10.35486/at.v13i1.168
Salem, G. S., Baiu, S. H., & Ali, A. A. (2023). Isolation, examination and characterization of actinomycetes as a source of antimicrobial agents from Libyan soil. Advances in Bioscience and Biotechnology, 14(6), 322-336. https://doi.org/10.4236/abb.2023.146020 DOI: https://doi.org/10.4236/abb.2023.146020
Sapkota, A., Thapa, A., Budhathoki, A., Sainju, M., Shrestha, P., & Aryal, S. (2020). Isolation, Characterization, and Screening of Antimicrobial-Producing Actinomycetes from Soil Samples. International Journal of Microbiology, 2020, 2716584. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/2716584 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/2716584
Schaeffer, A., & Wijntjes, C. (2022). Changed degradation behavior of pesticides when present in mixtures. Eco-Environment & Health, 1(1), 23-30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eehl.2022.02.002 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eehl.2022.02.002
Shahid, M., Manoharadas, S., Altaf, M., & Alrefaei, A. F. (2021). Organochlorine pesticides negatively influenced the cellular growth, morphostructure, cell viability, and biofilm-formation and phosphate-solubilization activities of Enterobacter cloacae strain EAM 35. ACS omega, 6(8), 5548-5559. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.0c05931 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.0c05931
Shalaby, A. A., Rahman, A. E., & Shalaby, M. A. (2022). Study of Imidacloprid, Azoxystrobin and Difenoconazole Residues and their Biochemical effects on Cucumber. Journal of Plant Protection and Pathology, 13(7), 161-167. https://dx.doi.org/10.21608/jppp.2022.148665.1085 DOI: https://doi.org/10.21608/jppp.2022.148665.1085
Sharma, I. (2021). Phytopathogenic fungi and their biocontrol applications. In Fungi Bio-Prospects in Sustainable Agriculture, Environment and Nano-Technology (pp. 155-188). Academic Press. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-821394-0.00007-X DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-821394-0.00007-X
Singh, B., Bhadu, A., Sharma, J., Ali, O., Neogi, S., Gunri, S. K., & Roy, D. (2022). Effect of microbes in enhancing the composting process: a review. International Journal of Plant & Soil Science, 34(23), 630-641. https://doi.org/10.9734/ijpss/2022/v34i232469 DOI: https://doi.org/10.9734/ijpss/2022/v34i232469
Singh, R., Shukla, A., Kaur, G., Girdhar, M., Malik, T., & Mohan, A. (2024). Systemic analysis of glyphosate impact on environment and human health. ACS Omega, 9(6), 6165-6183. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.3c08080 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.3c08080
Singh, S., Kumar, V., Gill, J. P. K., Datta, S., Singh, S., Dhaka, V., Kapoor, D., Wani, A. B., Dhanjal, D. S., Kumar, M., Harikumar, S. L., & Singh, J. (2020). Herbicide glyphosate: Toxicity and microbial degradation. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(20), 7519. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17207519 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17207519
Singh, T. B., Ali, A., Prasad, M., Yadav, A., Shrivastav, P., Goyal, D., & Dantu, P. K. (2020b). Role of organic fertilizers in improving soil fertility. In M. Naeem, A. A. Ansari, & S. S. Gill (eds.), Contaminants in Agriculture: Sources, Impacts and Management (pp. 61-77). Springer International Publishing. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-41552-5_3 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-41552-5_3
Singh, Y. P., Arora, S., Mishra, V. K., Gupta, R. H., & Mishra, S. J. (2023). Changes in physicochemical and microbial properties during standardization of on-farm composting of municipal solid waste. Journal of Natural Resource Conservation and Management, 4(1), 40-49. https://10.51396/ANRCM.4.1.2023.40-49 DOI: https://doi.org/10.51396/ANRCM.4.1.2023.40-49
Srinivasulu, M., Maddela, N. R., Chandra, M. S., Shankar, P. C., Rangaswamy, V., & Prasad, R. (2024). Microbe-pesticide interactions: Soil enzyme analysis and bacterial degradation of chlorpyrifos. Environmental Chemistry and Ecotoxicology, 6, 180-191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enceco.2024.05.004 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enceco.2024.05.004
Sun, J., Karuppiah, V., & Chen, J. (2020). The mechanism of heavy metal absorption and biodegradation of organophosphorus pesticides by Trichoderma. In V. K. Gupta, S. Zeilinger, H. B. Singh, & I. Druzhinina (eds.), New and future developments in microbial biotechnology and bioengineering (pp. 303-318). Elsevier. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-819453-9.00014-3 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-819453-9.00014-3
Sun, M., Yi, X., Tong, Z., Dong, X., Chu, Y., Meng, D., & Duan, J. (2023). Residual behavior and dietary risk assessment of chlorfenapyr and its metabolites in radish. Molecules, 28(2), 580. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28020580 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28020580
Tawfik Ali ElHaty, M., Ibrahim, M., & Mansour, M. (2022). Effectiveness of pesticides on soil fungal Biota and role of these fungi in bioremediation of pesticides residues. Alfarama Journal of Basic & Applied Sciences, 3(2), 239-252. https://doi.org/10.21608/ajbas.2022.118868.1086 DOI: https://doi.org/10.21608/ajbas.2022.118868.1086
Torres-Rodriguez, J. A., Reyes-Pérez, J. J., Quiñones-Aguilar, E. E., & Hernandez-Montiel, L. G. (2022). Actinomycete potential as biocontrol agent of phytopathogenic fungi: mechanisms, source, and applications. Plants, 11(23), 3201. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11233201 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11233201
Valle, A. L., Mello, F. C. C., Alves-Balvedi, R. P., Rodrigues, L. P., & Goulart, L. R. (2019). Glyphosate detection: methods, needs and challenges. Environmental Chemistry Letters, 17(1), 291-317. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-018-0789-5 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-018-0789-5
Van Gijn, K., Chen, Y. L., Van Oudheusden, B., Gong, S., De Wilt, H. A., Rijnaarts, H. H. M., & Langenhoff, A. A. M. (2021). Optimizing biological effluent organic matter removal for subsequent micropollutant removal. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 9(5), 106247. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2021.106247 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2021.106247
Wang, K., Sun, D. W., Pu, H., & Wei, Q. (2019). Surface-enhanced Raman scattering of core-shell Au@ Ag nanoparticles aggregates for rapid detection of difenoconazole in grapes. Talanta, 191, 449-456. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2018.08.005 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2018.08.005
Wang, W., Peng, G., Sun, Y., & Chen, X. (2024). Increasing the tolerance of Trichoderma harzianum T-22 to DMI fungicides enables the combined utilization of biological and chemical control strategies against plant diseases. Biological Control, 192, 105479. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocontrol.2024.105479 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocontrol.2024.105479
Wellington, E. M. H., & Toth, I. K. (1994). Actinomycetes. In R. W. Weaver, S. Angle, P. Bottomley, D. Bezdicek, S. Smith, A. Tabatabai & A. Wollum (eds.), Methods of Soil Analysis: Part 2 Microbiological and Biochemical Properties, 5 (pp. 269-290). https://doi.org/10.2136/sssabookser5.2.c15 DOI: https://doi.org/10.2136/sssabookser5.2.c15
Williams, S. T., & Cross, T. (1971). Chapter XI actinomycetes. In Methods in microbiology (pp. 295-334). Academic Press. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0580-9517(09)70016-9 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0580-9517(09)70016-9
Wu, P., Zhao, R., Zhang, X., Niu, T., Cao, B., Zhu, F., Li, N., Zhang, Y., Wu, Y., & Wang, Y. (2020). Rhodopseudomonas capsulata enhances cleaning of chlorfenapyr from environment. Journal of Cleaner Production, 259, 120271. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.120271 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.120271
Xu, C., Cui, D., Lv, X., Zhong, G., & Liu, J. (2023). Heterogeneous distribution of carbofuran shaped by Pseudomonas stutzeri biofilms enhances biodegradation of agrochemicals. Environmental Research, 229, 115894. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2023.115894 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2023.115894
Xu, J., Smith, S., Smith, G., Wang, W., & Li, Y. (2019). Glyphosate contamination in grains and foods: An overview. Food Control, 106, 106710. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0956713519302919 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2019.106710
Xu, P., Shu, L., Yang, Y., Kumar, S., Tripathi, P., Mishra, S., Qiu, C., Li, Y., Wu, Y., & Yang, Z. (2024). Microbial agents obtained from tomato straw composting effectively promote tomato straw compost maturation and improve compost quality. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 270, 115884. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2023.115884 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2023.115884
Yang, J., Luo, F., Zhou, L., Sun, H., Yu, H., Wang, X., Zhang, X., Yang, M., Lou, Z., & Chen, Z. (2020). Residue reduction and risk evaluation of chlorfenapyr residue in tea planting, tea processing, and tea brewing. Science of The Total Environment, 738, 139613. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.139613 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.139613
Zhan, Y., Chang, Y., Tao, Y., Zhang, H., Lin, Y., Deng, J., Ma, T., Ding, G., Wei, Y., & Li, J. (2022). Insight into the dynamic microbial community and core bacteria in composting from different sources by advanced bioinformatics methods. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 30(4), 8956-8966. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-20388-7 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-20388-7
Zhang, J., Shen, C., Shang, T. H., & Liu, J. L. (2022). Difference responses of soil fungal communities to cattle and chicken manure composting application. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 133(2), 323-339. https://doi.org/10.1111/jam.15549 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/jam.15549
Zhao, X., Wei, Y., Fan, Y., Zhang, F., Tan, W., He, X., & Xi, B. (2018). Roles of bacterial community in the transformation of dissolved organic matter for the stability and safety of material during sludge composting. Bioresource technology, 267, 378-385. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2018.07.060 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2018.07.060
Zin, N. A., & Badaluddin, N. A. (2020). Biological functions of Trichoderma spp. for agriculture applications. Annals of Agricultural Sciences, 65(2), 168-178. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aoas.2020.09.003 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aoas.2020.09.003