Relaciones ambientes–sociedad en playas turísticas de Ecuador: aplicación de criterios “Plata y Oro” en Paraíso y Puerto Engabao
Contenido principal del artículo
Resumen
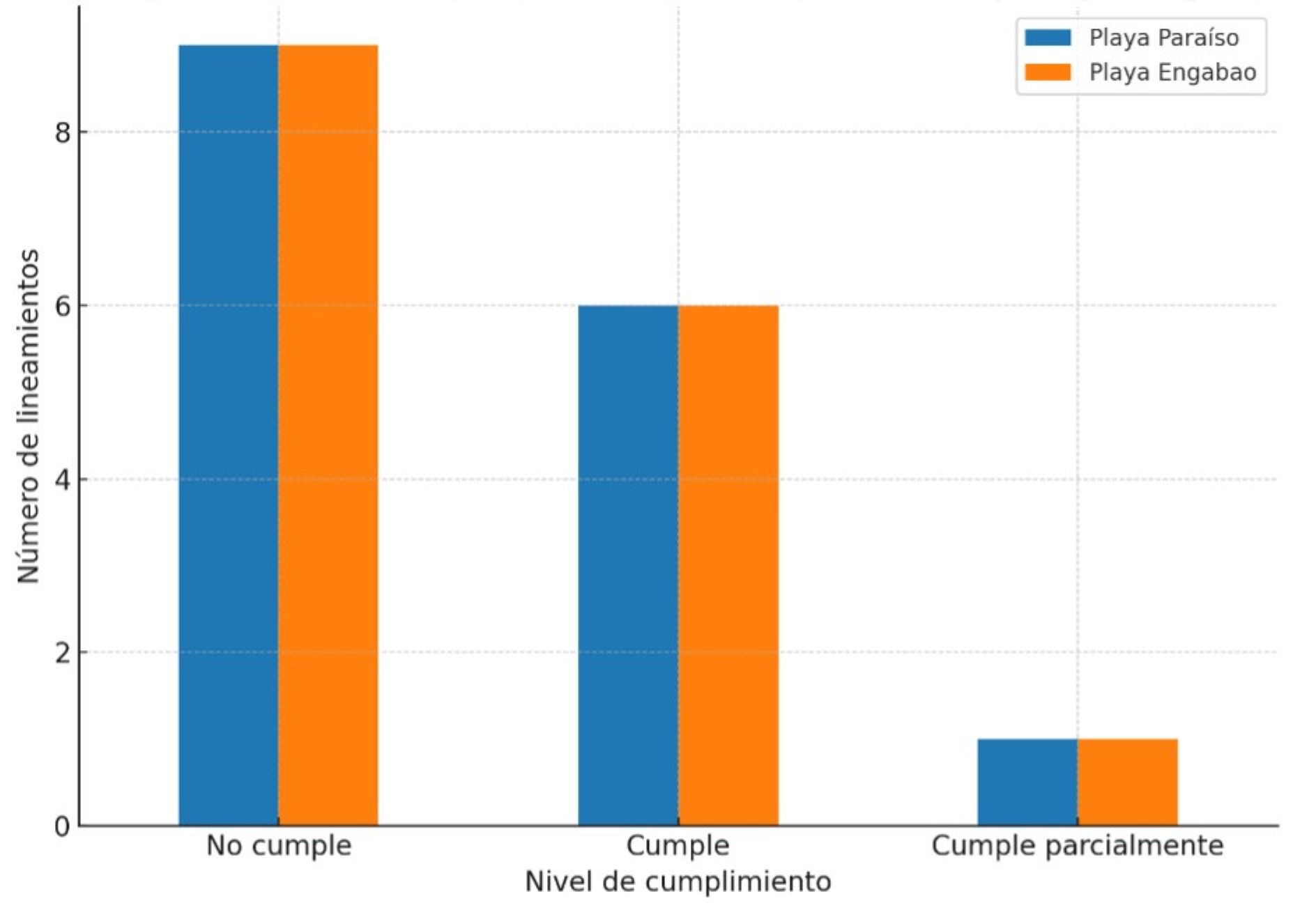
En Ecuador, las playas son un recurso importante para el turismo costero, pero en la actualidad enfrentan retos evidentes como la contaminación, los impactos del cambio climático y una planificación territorial insuficiente, lo que compromete su sostenibilidad y por lo tanto reduce su competitividad. Este estudio evaluó el cumplimiento del Acuerdo Ministerial No. 2022-030, que establece los requisitos y el proceso para la obtención del reconocimiento como “Playa Turística Sostenible - Ecuador” con la Ficha de Requisitos Específicos para obtener el Reconocimiento de Playas Turísticas Sostenibles “Plata y Oro”, en Playa Paraíso y Playa Engabao, en el cantón Playas, Ecuador. Se aplicó un enfoque descriptivo-comparativo, recopilando información a través de visitas de campo, observaciones directas y análisis documental. Los criterios que fueron evaluados son: seguridad, servicios turísticos, gestión ambiental y gestión costera. Los resultados muestran que Playa Paraíso tiene mejores condiciones en seguridad e infraestructura básica, mientras que Puerto Engabao muestra deficiencias en gestión ambiental y ordenamiento territorial. Ninguna de las dos playas evaluadas alcanzó el nivel de certificación “Oro”. Se concluye que estos hallazgos resaltan la necesidad de reforzar la gestión ambiental, turística y social para conseguir un desarrollo costero sostenible.
Descargas
Métricas
Detalles del artículo

Esta obra está bajo una licencia internacional Creative Commons Atribución-NoComercial 4.0.
Los autores que publican en Siembra conocen y aceptan las siguientes condiciones:
- Los autores retienen los derechos de copia (copyright) y ceden a Siembra el derecho de primera publicación del trabajo, bajo licencia Creative Commons Attribution License, que permite a terceros utilizar lo publicado siempre que hagan referencia al autor o autores del trabajo y a su publicación en esta revista.
![]() Esta obra está bajo una Licencia Creative Commons Reconocimiento-NoComercial 4.0 Internacional (CC BY-NC 4.0).
Esta obra está bajo una Licencia Creative Commons Reconocimiento-NoComercial 4.0 Internacional (CC BY-NC 4.0).
- Los autores conservan los derechos de autor y garantizan a Siembra el derecho de publicar el manuscrito a través de los canales que considere adecuados.
- Los autores pueden establecer por su cuenta acuerdos adicionales para la distribución no exclusiva de la versión de la obra publicada en Siembra, haciendo reconocimiento de su publicación inicial en la misma, como por ejemplo en repositorios institucionales.
Se autoriza a los autores a difundir sus trabajos electrónicamente una vez sea aceptado el manuscrito para su publicación.
Citas
Acuerdo Ministerial No. 2022 030. Para el reconocimiento de “Playa Turística Sostenible - Ecuador”. Registro Oficial No. 212 14. 19 de diciembre de 2022 (Ecuador). https://www.gob.ec/sites/default/files/regulations/2022-12/RO%20Playas%20tur%C3%ADsticas%20sostenibles_compressed.pdf
Allen, C., Malekpour, S., y Mintrom, M. (2023). Cross‐scale, cross‐level and multi‐actor governance of transformations toward the Sustainable Development Goals: A review of common challenges and solutions. Sustainable Development, 31(3), 1250–1267. https://doi.org/10.1002/sd.2495 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/sd.2495
Ansell, C., y Gash, A. (2008). Collaborative governance in theory and practice. Journal of Public Administration Research and Theory, 18(4), 543–571. https://doi.org/10.1093/jopart/mum032 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/jopart/mum032
Basurto-Cedeno, E., Penington-Gray, L., y Basurto, X. (2025). Developing a comprehensive index for beaches to enhance sustainability and visitor experience through holistic monitoring. Sustainability, 17(7), 3049. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17073049 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/su17073049
Berkes, F., y Folke, C. (1998). Linking social and ecological systems: Management practices and social mechanisms for building resilience. Cambridge University Press. https://assets.cambridge.org/97805217/85624/excerpt/9780521785624_excerpt.pdf
Bramwell, B., y Lane, B. (2011). Critical research on the governance of tourism and sustainability. Journal of Sustainable Tourism, 19(4–5), 411–421. https://doi.org/10.1080/09669582.2011.580586 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/09669582.2011.580586
Cicin-Sain, B., y Knecht, R. W. (1998). Integrated coastal and ocean management: Concepts and practices. Island Press. https://islandpress.org/books/integrated-coastal-and-ocean-management#desc
Er-Ramy, N., Nachite, D., Anfuso, G., y Azaaouaj, S. (2023). The Sector Analysis as a coastal management tool for sustainable tourism development on the Mediterranean Coast of Morocco. Sustainability, 15(16), 12581. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151612581 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/su151612581
Global Sustainable Tourism Council [GSTC]. (2020). GSTC criteria for destinations. GSTC. https://www.gstcouncil.org
Halliday, E., y Gast, R. J. (2011). Bacteria in beach sands: An emerging challenge in protecting coastal water quality and bather health. Environmental Science & Technology, 45(2), 370–379. https://doi.org/10.1021/es102747s DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/es102747s
Iturralde, G., y Samaniego, J. (2021). Marine spatial planning in Ecuador: Current situation and the challenges we face. Revista Costas, 6(Esp. 2), 293–314. https://doi.org/10.26359/costas.e1421 DOI: https://doi.org/10.26359/costas.e1421
Jones, A., y Phillips, M. (eds.). (2018). Global climate change and coastal tourism: recognizing problems, managing solutions and future expectations. CABI. https://doi.org/10.1079/9781780648439.0000 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1079/9781780648439.0000
Kozak, M., Crotts, J. C., y Law, R. (2007). The impact of the perception of risk on international travellers. International Journal of Tourism Research, 9(4), 233–242. https://doi.org/10.1002/jtr.607 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/jtr.607
Lastra-Bravo, X., y Cabanilla V., E. (2020). Impacto del turismo en el desarrollo del Ecuador: Reflexiones desde la academia – IV CONGRETUR. Estudios y Perspectivas en Turismo, 29(4), 1272–1289. https://www.redalyc.org/journal/1807/180766099014/html/
Marchese, L., Botero, C. M., Zielinski, S., Anfuso, G., Polette, M., y Correa, I. C. S. (2021). Beach certification schemes in Latin America: Are they applicable to the Brazilian context? Sustainability, 13(2), 934. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13020934 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/su13020934
Mcleod, E., Chmura, G. L., Bouillon, S., Salm, R., Björk, M., Duarte, C. M., Lovelock, C. E., Schlesinger, W. H., y Silliman, B. R. (2011). A blueprint for blue carbon: toward an improved understanding of the role of vegetated coastal habitats in sequestering CO2. Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment, 9(10), 552–560. https://doi.org/10.1890/110004 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1890/110004
Mora Méndez, F. M., García Castro, S. R., y Chiriboga Cisneros, E. F. (2020). Certificación turística como herramienta de diferenciación clave para las playas: Caso Playa Chipipe. Salinas- Ecuador. INNOVA Research Journal, 5(3), 233–244. https://doi.org/10.33890/innova.v5.n3.2020.1386 DOI: https://doi.org/10.33890/innova.v5.n3.2020.1386
Ocean Panel. (2022). Opportunities for transforming coastal and marine tourism: Towards sustainability, regeneration and resilience. Ocean Panel. https://oceanpanel.org/wp-content/uploads/2022/06/Sustainable-Tourism-Full-Report.pdf
Ostrom, E. (1990). Governing the commons: The evolution of institutions for collective action. Cambridge University Press. https://www.actu-environnement.com/media/pdf/ostrom_1990.pdf DOI: https://doi.org/10.1017/CBO9780511807763
Pine, B. J., y Gilmore, J. H. (2013). The experience economy: past, present and future. En J. Sundbo y F. Sørensen (eds.), Handbook on the Experience Economy (pp. 21-44). Edward Elgar Publishing. https://doi.org/10.4337/9781781004227.00007 DOI: https://doi.org/10.4337/9781781004227.00007
Rhodes, R. A. W. (1996). The New Governance: Governing without Government. Political Studies, 44(4), 652–667. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-9248.1996.tb01747.x DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-9248.1996.tb01747.x
Roca, E., y Villares, M. (2008). Public perceptions for evaluating beach quality in urban and semi-natural environments. Ocean & Coastal Management, 51(4), 314–329. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ocecoaman.2007.09.001 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ocecoaman.2007.09.001
Senthilkumar, R. (2021). Sustainable coastal tourism – An overview. Sustainability, Agri, Food and Environmental Research, 10(1), 1–12. https://doi.org/10.7770/safer-V10N1-art2497 DOI: https://doi.org/10.7770/safer-V10N1-art2497
Sharpley, R. (2020). Tourism, sustainable development and the theoretical divide: 20 years on. Journal of Sustainable Tourism, 28(11), 1932–1946. https://doi.org/10.1080/09669582.2020.1779732 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/09669582.2020.1779732
Slovic, P. (1987). Perception of Risk. Science, 236(4799), 280–285. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.3563507 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1126/science.3563507
United Nations Environment Programme [UNEP]. (2013). Review of ecosystem-based indicators and indices on the state of the Regional Seas. UNEP (DEPI)/VW.1/INF.1. UNEP. https://www.unep.org/resources/report/review-ecosystem-based-indicators-and-indices-state-regional-seas-0
Whitman, R. L., Harwood, V. J., Edge, T. A., Nevers, M. B., Byappanahalli, M., Vijayavel, K., Brandão, J., Sadowsky, M. J., Alm, E. W., Crowe, A., Ferguson, D., Ge, Z., Halliday, E., Kinzelman, J., Kleinheinz, G., Przybyla-Kelly, K., Staley, C., Staley, Z., y Solo-Gabriele, H. M. (2014). Microbes in beach sands: integrating environment, ecology and public health. Reviews in Environmental Science and Bio/Technology, 13(3), 329–368. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11157-014-9340-8 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11157-014-9340-8
World Health Organization. (2021). Guidelines on recreational water quality: Volume 1 – Coastal and fresh waters. Geneva: World Health Organization. https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240031302
Zielinski, S., y Botero, C. (2015). Are eco-labels sustainable? Beach certification schemes in Latin America and the Caribbean. Journal of Sustainable Tourism, 23(10), 1550–1572. https://doi.org/10.1080/09669582.2015.1047376 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/09669582.2015.1047376